Azure Event Hubs EARLY ACCESS
The following tutorial describes the steps to sync CDC data from YugabyteDB Anywhere to your Azure Synapse Analytics workspace using Azure offerings such as Azure Event Hubs and Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2.
Reference architecture
The following diagram shows how to move YugabyteDB Anywhere CDC data to an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace.
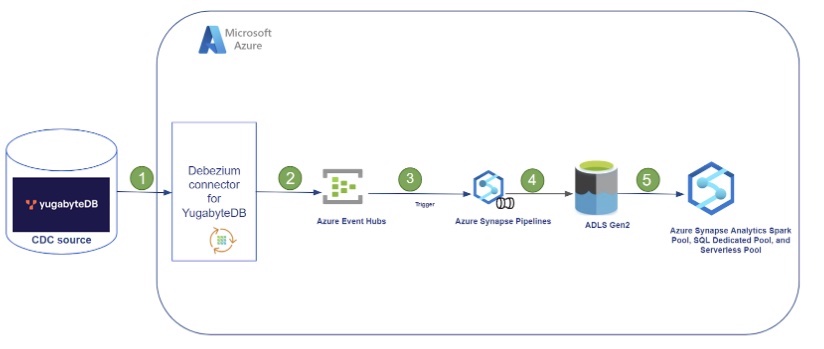
The following table describes the components.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| YugabyteDB Anywhere | Yugabyte self-managed DBaaS for deploying YugabyteDB at scale that includes YugabyteDB's self-managed, stateless CDC functionality with support for Confluent Kafka Connect. A pull-based model is used to report changes from the database Write-Ahead-Log (WAL). For more information on CDC, refer to Change Data Capture. |
| Debezium connector | Pulls data from YugabyteDB, publishes it to Kafka, and runs in a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine. |
| Azure Event Hubs | Azure big data streaming platform and event ingestion service. |
| Azure Synapse Pipelines | context=%2Fazure%2Fsynapse-analytics%2Fcontext%2Fcontext&tabs=synapse-analytics |
| ADLS Gen2 | Storage account |
| Azure Synapse workspace | Azure integrated platform service that merges the capabilities of data lakes, data integrations for ETL/ELT pipelines, analytics tools, and services. |
The following table describes how the data flows through each of these components.
| Step | Component | Operation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Debezium YugabyteDB Kafka Connect | Stream the changed data sets requested from the source YugabyteDB Anywhere YSQL Tables. |
| 2 | Azure Event Hubs | Stream messages from Kafka to different targets. |
| 3 | Azure Synapse Analytics Pipeline | Used to schedule data-driven workflows that can ingest data from Azure Event Hubs to an Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 account. |
| 4 | ADLS (Azure Data Lake Services) Gen2 | CDC data from the Azure Event Hub is saved to ADLS Gen2 in Parquet format. |
| 5 | Azure Synapse workspace | Azure SQL Pools and Spark Pools can be used to analyze the CDC data from Yugabyte in near real time. |
Prerequisites
To get started, you'll need the following:
- YugabyteDB Anywhere database with CDC enabled.
- An Azure Event Hubs instance.
- An Azure Synapse Analytics workspace with SQL Pools and Spark Pools. Tables can be created in the SQL Pools to house the CDC data.
- An Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. The YugabyteDB CDC data resides in this Storage account and can be queried using external tables in Synapse SQL Pools.
Get Started
Use the following steps to move YugabyteDB CDC data into Azure Synapse Analytics using the YugabyteDB Debezium Connector that streams data into Azure Event Hubs. This data can be stored as Avro/JSON/Parquet in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 and then accessed via SQL Pools or Spark Pools in the Synapse workspace.
Step 1: Create an Event Hubs namespace and Event Hubs
Azure Event Hubs will be used to capture the CDC data from YugabyteDB. To create Event Hubs namespace and Event Hubs, refer to the Quickstart instructions in the Microsoft documentation. Save the Event Hubs connection string and fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for later use. For instructions, see Get an Event Hubs connection string.
Step 2: Create a YugabyteDB CDC Connector
Now that you have created Event Hubs in Azure, you need to create a YugabyteDB CDC Connector that will capture the changes in the Yugabyte database and send them to Event Hubs. Perform the following steps to create a YugabyteDB CDC Connector:
-
Add data and tables to YugabyteDB. After this is done, create the CDC Stream ID using the yb-admin command.
-
Configure your event hub to connect and receive data from the Debezium Connector for Yugabyte. You can create an Azure Event Hub configuration file that will be saved locally on the machine, for example you can save the configuration file as
eventhub.configin the Kafkabindirectory. For more details on creating your configuration file, refer to the sample available in the Kafka Connect for Event Hubs documentation. -
Download the Debezium connector jar file from the Yugabyte GitHub repository (https://github.com/yugabyte/debezium-connector-yugabytedb/releases/download/v1.9.5.y.19/debezium-connector-yugabytedb-1.9.5.y.19.jar). Save this jar file in your Kafka
libsfolder (for example,/home/azureuser/kafka_2.12-3.2.0/libs). -
Navigate to the Kafka bin directory (for example, /home/azureuser/kafka_2.12-3.2.0/bin) on your machine and run the following command:
./connect-distributed.sh <Event Hub configuration file>This command starts YugabyteDB Debezium Kafka Connect.
-
Create a Kafka Connector by running the following commands:
curl -i -X POST -H "Accept:application/json" -H "Content-Type:application/json" \ localhost:8083/connectors/ \ -d '{ "name": "ybconnector", "config": { "connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.YugabyteDBConnector", "database.hostname":"'$IP'", "database.port":"5433", "database.master.addresses": "'$IP':7100", "database.user": "yugabyte", "database.password": "yugabyte", "database.dbname" : "yugabyte", "database.server.name": "<db server name>", "table.include.list":"public.your table name", "database.streamid":your generated stream id", "snapshot.mode":"never" } }'Replace the StreamID and database details as needed. Additionally, replace the $IP variable with your YugabyteDB address or DNS Name.
Step 3: Configure the YugabyteDB CDC Connector
After you have created the YugabyteDB CDC Connector, you must configure it to send CDC data to Azure Event Hubs.
To connect the CDC Connector to Event Hubs, edit the config.yaml file in the directory where you created the YugabyteDB CDC Connector, with the following parameters:
dest_conf: Connection string for the event hub. You can find this connection string in the Azure portal by navigating to Event Hubs > Shared access policies, click RootManageSharedAccessKey and copy the "Connection string - primary key".batch_size: Maximum number of events that can be sent in a single batch.batch_timeout_ms: Maximum time (in milliseconds) that can elapse before a batch is sent, even if it is not full.consumer_threads: Number of threads that the CDC Connector will use to consume events from YugabyteDB. Set this value based on the number of cores on your machine.poll_interval_ms: Interval (in milliseconds) at which the CDC Connector will check for new events in the Yugabyte database.
Step 4: Run the YugabyteDB CDC Connector
Start the YugabyteDB CDC Connector using the following command:
sql $ yb-connect-cdc start --cdc_dir <directory>
Replace
Step 5: Pull Events From Azure EventHubs
You have several options to move data from Azure Event Hubs to a Synapse workspace. An option using Azure Synapse Pipelines in a Spark Notebook is described in the following section.
Use Azure Synapse Pipelines with Event Hubs
An Azure Synapse pipeline, which subscribes to changes in Event Hubs via a custom trigger, can be used to move CDC data into an ADLS Gen 2 account. One option to accomplish this is to create a Spark Notebook from Azure Synapse Studio which connects to Event Hubs for the specific topic(s) and stores the data in an ADLS Gen2 folder.
Following is a sample code for a PySpark Notebook for an IoT management application, which pulls data from each of the event hubs every five minutes for analysis. This Python code will pull the messages from the event hub and persist them in ADLS Gen2.
# Event Hub Connection String with the topic name as db
ehConf = {}
connectionString ="Endpoint=sb://<dbname>.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=xxxxxx;SharedAccessKey=xxxx;EntityPath=<dbserver>"
ehConf['eventhubs.connectionString'] = connectionString
# Add consumer group to the ehConf dictionary
ehConf['eventhubs.consumerGroup'] = "$Default"
from pyspark.sql.types import *
from pyspark.sql.functions import *
from pyspark.sql.functions import unbase64,base64
from pyspark.sql.functions import *
from pyspark.sql.types import *
import json
# ADLS Gen2 Folder Name
checkpointpath = '/mnt/delta/source/<path>/_checkpoints'
write_path ='/mnt/delta/source/<path>'
# Start from beginning of stream
startOffset = "-1"
# End at the current time. This datetime formatting creates the correct string format from a python datetime object
#endTime = dt.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%fZ")
startingEventPosition = {
"offset": startOffset,
"seqNo": -1, #not in use
"enqueuedTime": None, #not in use
"isInclusive": True
}
conf = {}
conf["eventhubs.connectionString"] = sc._jvm.org.apache.spark.eventhubs.EventHubsUtils.encrypt(connectionString)
conf["eventhubs.consumerGroup"] = "$Default"
conf["eventhubs.startingPosition"] = json.dumps(startingEventPosition)
df = spark \
.readStream \
.format("eventhubs") \
.options(**conf) \
.load()
df = df.withColumn("body", df["body"].cast("string")
df1= df.select(get_json_object(df['body'],"$.payload.before.eventid.value").alias('beforeeventid'), get_json_object(df['body'],"$.payload.after.eventid.value").alias('eventid'),get_json_object(df['body'],"$.payload.after.sensor_uuid.value").alias('sensor_uuid'),get_json_object(df['body'],"$.payload.after.humidity.value").alias('humidity'),get_json_object(df['body'],"$.payload.op").alias('Operation'))
df2=df1.select(eventid','sensor_uuid','humidity','operation', when(df1.Operation =='d',df1.beforeeventid).otherwise(df1.eventid).alias('eventid'))
#Save the data in Delta Format
query = (df2.writeStream.format('delta') \
.option('checkpointLocation',checkpointpath) \
.option("path", write_path) \
.outputMode("append") \
.start()
)
Save and execute this code snippet in the Azure Synapse Analytics Workspace using a Spark Pool with Pyspark as the language after making any appropriate changes.
You can analyze the data in the ADLS Gen2 account using Spark pools as described in Query captured data in Parquet format with Azure Synapse Analytics Spark Pools.
Step 6: View CDC Data in Azure Synapse Dedicated SQL Pools or Spark Pools
You can choose to view the CDC data stored in the ADLS Gen 2 account using either Synapse SQL Dedicated or Serverless Pools.
To do this, follow the instructions in the Microsoft documentation: