Redpanda EARLY ACCESS
Redpanda is an open-source distributed streaming platform designed to be fast, scalable, and efficient. It is built using modern technologies like Rust, and is designed to handle large volumes of data in real time. Redpanda is similar to other messaging systems like Apache Kafka, but with some key differences, including the following:
-
Performance: Redpanda is designed for high-performance and low-latency, with a focus on optimizing performance for modern hardware. Redpanda uses a zero-copy design, which eliminates the need to copy data between kernel and user space. This provides faster and more efficient data transfer.
-
Scalability: Redpanda is designed to scale horizontally and vertically. It also supports multi-tenancy, which allows multiple applications to share the same cluster.
-
Storage: Redpanda stores data in a columnar format, which allows for more efficient storage and faster query times. This also enables Redpanda to support SQL-like queries on streaming data.
-
Security: Redpanda includes built-in security features such as TLS encryption and authentication, while Kafka relies on third-party tools for security.
-
API compatibility: Redpanda provides an API that is compatible with the Kafka API, so you can migrate from Kafka to Redpanda without having to change existing applications.
The following tutorial describes how to integrate YugabyteDB CDC Connector with Redpanda.
YugabyteDB CDC using Redpanda Architecture
The following diagram shows the end-to-end integration architecture of YugabyteDB CDC using Redpanda.
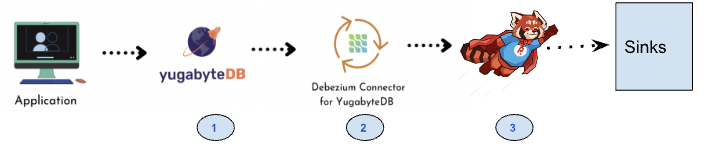
The following table describes how the data flows through each of these components.
| Step | Operations/Tasks | Component |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CDC Enabled and Create the Stream ID for specific YSQL database. | YugabyteDB |
| 2 | Install and configure Redpanda and download YugabyteDB Debezium Connector. | Redpanda Cloud or Redpanda Docker YugabyteDB CDC Connector |
| 3 | Create and Deploy connector configuration in Redpanda. | Redpanda, Kafka Connect |
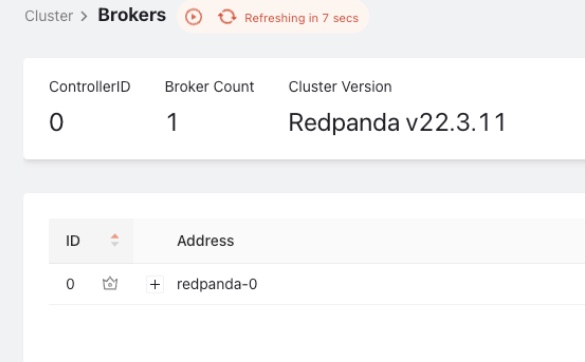
Set up Redpanda with YugabyteDB CDC
Install YugabyteDB
You have multiple options to install or deploy YugabyteDB.
If you're running a Windows Machine then you can leverage Docker on Windows with YugabyteDB.
Install and set up Redpanda
Follow the Redpanda Quick Start to spin up the Redpanda cluster using single- or multi-broker configuration using docker-compose or using a Redpanda cloud account.
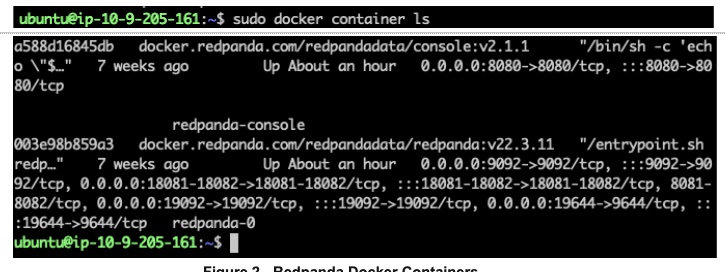
Post installation and setup using the docker option, you can see docker containers are up and running. The following illustration shows two docker containers (Redpanda-Console and Redpanda Broker):
Deploy YugabyteDB Debezium connector (docker container)
Link the Redpanda Broker address with YugabyteDB Debezium connector as follows;
sudo docker run -it --rm --name connect --net=host -p 8089:8089 -e GROUP_ID=1 -e BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS=127.0.0.1:19092 -e CONNECT_REST_PORT=8082 -e CONNECT_GROUP_ID="1" -e CONFIG_STORAGE_TOPIC=my_connect_configs -e OFFSET_STORAGE_TOPIC=my_connect_offsets -e STATUS_STORAGE_TOPIC=my_connect_statuses -e CONNECT_KEY_CONVERTER="org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter" -e CONNECT_VALUE_CONVERTER="org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter" -e CONNECT_INTERNAL_KEY_CONVERTER="org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter" -e CONNECT_INTERNAL_VALUE_CONVERTER="org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter" -e CONNECT_REST_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME="connect" quay.io/yugabyte/debezium-connector:latest
Deploy the source connector using Redpanda
Create and deploy the source connector as follows, changing the parameters as per your configuration:
curl -i -X POST -H "Accept:application/json" -H "Content-Type:application/json" localhost:8083/connectors/ -d '{
"name": "srcdb",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.YugabyteDBConnector",
"database.hostname":"10.9.205.161",
"database.port":"5433",
"database.master.addresses": "10.9.205.161:7100",
"database.user": "yugabyte",
"database.password": "xxxx",
"database.dbname" : "testcdc",
"database.server.name": "dbeserver5",
"table.include.list":"public.balaredpandatest",
"database.streamid":"d36ef18084ed4ad3989dfbb193dd2546",
"snapshot.mode":"initial",
"transforms": "unwrap",
"transforms.unwrap.type": "io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.transforms.YBExtractNewRecordState",
"transforms.unwrap.drop.tombstones": "false",
"time.precision.mode": "connect",
"key.converter":"io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter",
"key.converter.schema.registry.url":"http://localhost:18081",
"key.converter.enhanced.avro.schema.support":"true",
"value.converter":"io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter",
"value.converter.schema.registry.url":"http://localhost:18081",
"value.converter.enhanced.avro.schema.support":"true"
}
}'
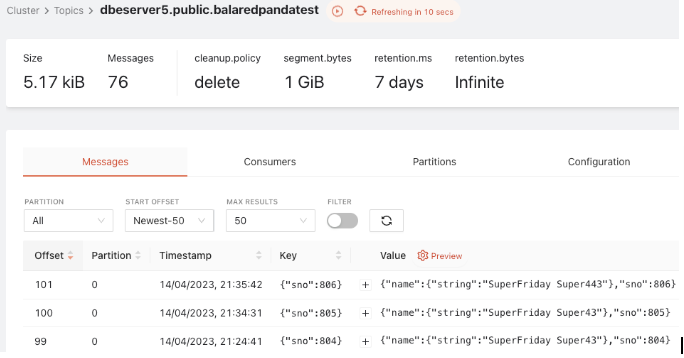
Monitor the messages through Redpanda
The following illustration shows the Redpanda broker details installed locally using Docker and the topic that was subscribed (for example, dbeserver5.public.balaredpandatest) and the schema registry with key and value details of the topic.