Quick start
The local cluster setup on a single host is intended for development and learning. For production deployment, performance benchmarking, or deploying a true multi-node on multi-host setup, see Deploy YugabyteDB.
Install YugabyteDB
Installing YugabyteDB involves completing prerequisites and downloading the YugabyteDB package.
Prerequisites
Before installing YugabyteDB, ensure that you have the following available:
-
One of the following operating systems:
-
CentOS 7 or later
-
Ubuntu 16.04 or later
-
-
Python 3. To check the version, execute the following command:
python --versionPython 3.7.3By default, CentOS 8 does not have an unversioned system-wide
pythoncommand. To fix this, setpython3as the alternative forpythonby runningsudo alternatives --set python /usr/bin/python3.Starting from Ubuntu 20.04,
pythonis no longer available. To fix this, runsudo apt install python-is-python3. -
wgetorcurl.The instructions use the
wgetcommand to download files. If you prefer to usecurl, you can replacewgetwithcurl -O.To install
wget:- On CentOS, run
yum install wget - On Ubuntu, run
apt install wget
To install
curl:- On CentOS, run
yum install curl - On Ubuntu, run
apt install curl
- On CentOS, run
ulimits
Because each tablet maps to its own file, you can create a very large number of files in the current shell by experimenting with several hundred tables and several tablets per table. You need to configure ulimit values.
Download YugabyteDB
YugabyteDB supports both x86 and ARM (aarch64) CPU architectures. Download packages ending in x86_64.tar.gz to run on x86, and packages ending in aarch64.tar.gz to run on ARM.
The following instructions are for downloading the Preview release of YugabyteDB, which is recommended for development and testing only. For other versions, see Releases.
Download YugabyteDB as follows:
-
Download the YugabyteDB package using one of the following
wgetcommands:wget https://downloads.yugabyte.com/releases/2.17.3.0/yugabyte-2.17.3.0-b152-linux-x86_64.tar.gzOr:
wget https://downloads.yugabyte.com/releases/2.17.3.0/yugabyte-2.17.3.0-b152-el8-aarch64.tar.gz -
Extract the package and then change directories to the YugabyteDB home.
tar xvfz yugabyte-2.17.3.0-b152-linux-x86_64.tar.gz && cd yugabyte-2.17.3.0/Or:
tar xvfz yugabyte-2.17.3.0-b152-el8-aarch64.tar.gz && cd yugabyte-2.17.3.0/
Configure YugabyteDB
To configure YugabyteDB, run the following shell script:
./bin/post_install.sh
Create a local cluster
To create a single-node local cluster with a replication factor (RF) of 1, run the following command:
./bin/yugabyted start
After the cluster has been created, clients can connect to the YSQL and YCQL APIs at http://localhost:5433 and http://localhost:9042 respectively. You can also check ~/var/data to see the data directory and ~/var/logs to see the logs directory.
If you have previously installed YugabyteDB 2.8 or later and created a cluster on the same computer, you may need to upgrade the YSQL system catalog to run the latest features.
Check the cluster status
Execute the following command to check the cluster status:
./bin/yugabyted status
Expect an output similar to the following:
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| yugabyted |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Status : Running. Leader Master is present |
| Web console : http://127.0.0.1:7000 |
| JDBC : jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5433/yugabyte?user=yugabyte&password=yugabyte |
| YSQL : bin/ysqlsh -U yugabyte -d yugabyte |
| YCQL : bin/ycqlsh -u cassandra |
| Data Dir : /Users/myuser/var/data |
| Log Dir : /Users/myuser/var/logs |
| Universe UUID : fad6c687-e1dc-4dfd-af4b-380021e19be3 |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Use the Admin UI
The cluster you have created consists of two processes: YB-Master which keeps track of various metadata (list of tables, users, roles, permissions, and so on) and YB-TServer which is responsible for the actual end-user requests for data updates and queries.
Each of these processes exposes its own Admin UI that you can use to check the status of the corresponding process, and perform certain administrative operations. The UIs are available via your local machine's IP address, as displayed in the Web console output of the status command you ran.
The YB-Master Admin UI uses port 7000 and is typically at http://127.0.0.1:7000, while the YB-TServer Admin UI uses port 9000 and is typically at http://127.0.0.1:9000.
Overview and YB-Master status
The following illustration shows the YB-Master home page with a cluster with a replication factor of 1, a single node, and no tables. The YugabyteDB version is also displayed.
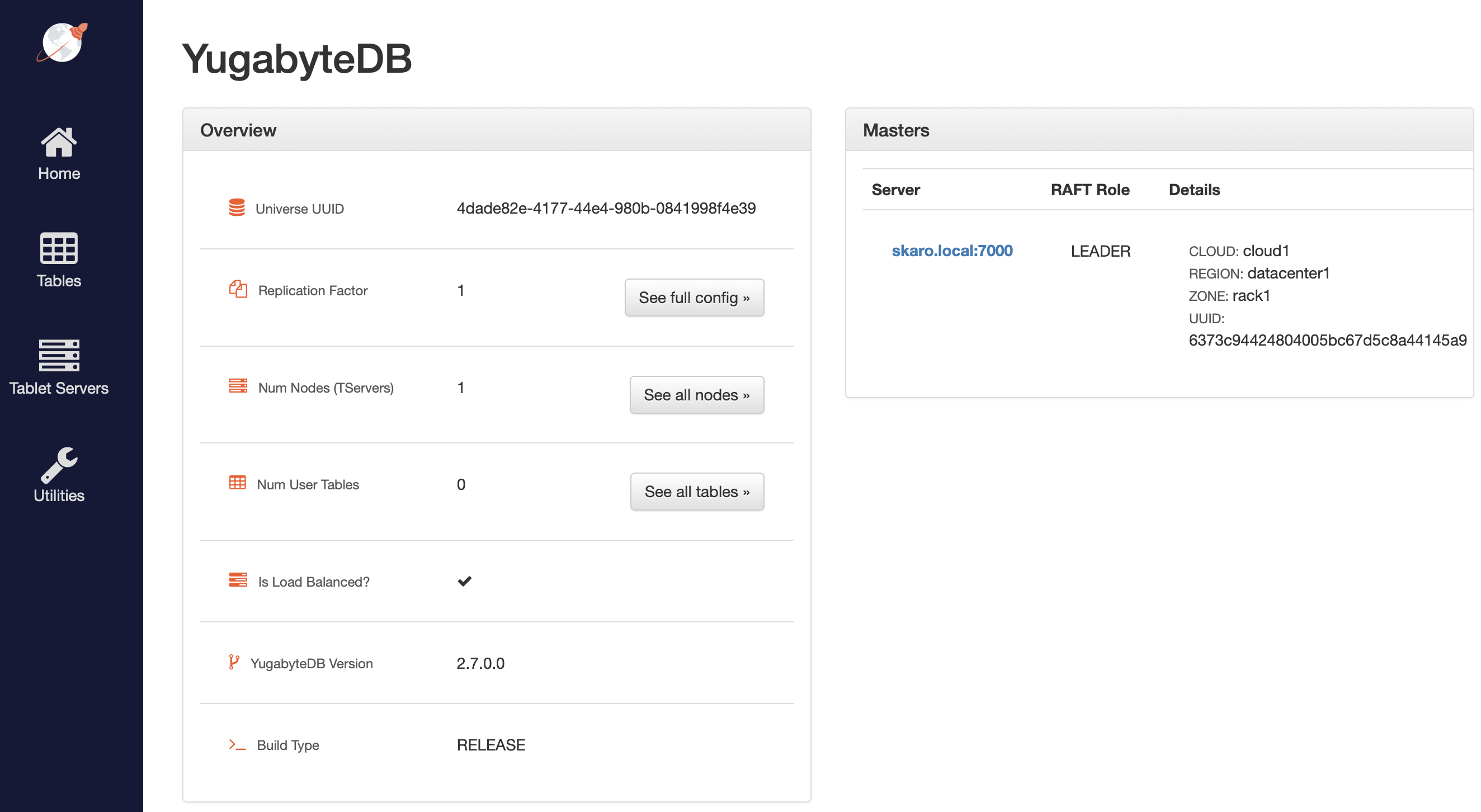
The Masters section highlights the 1 YB-Master along with its corresponding cloud, region, and zone placement.
YB-TServer status
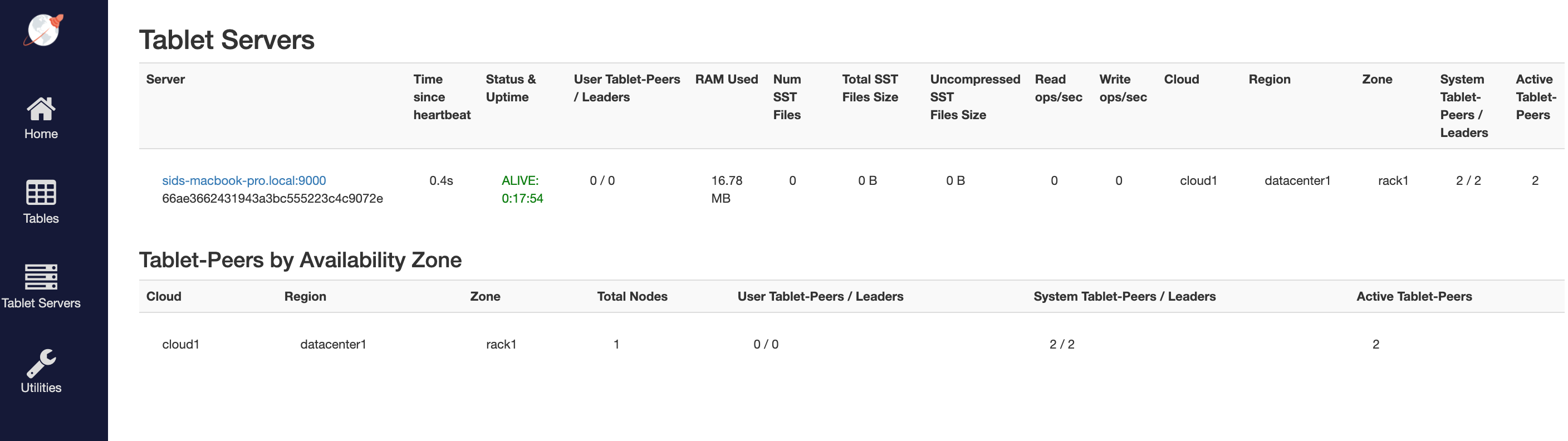
Click See all nodes to open the Tablet Servers page that lists the YB-TServer along with the time since it last connected to the YB-Master using regular heartbeats. Because there are no user tables, User Tablet-Peers / Leaders is 0. As tables are added, new tablets (also known as shards) will be created automatically and distributed evenly across all the available tablet servers.
Connect to the database
Using the YugabyteDB SQL shell, ysqlsh, you can connect to your cluster and interact with it using distributed SQL. ysqlsh is installed with YugabyteDB and is located in the bin directory of the YugabyteDB home directory.
To open the YSQL shell, run ysqlsh.
$ ./bin/ysqlsh
ysqlsh (11.2-YB-2.1.0.0-b0)
Type "help" for help.
yugabyte=#
To load sample data and explore an example using ysqlsh, refer to Retail Analytics.
Build an application
Applications connect to and interact with YugabyteDB using API client libraries (also known as client drivers). This section shows how to connect applications to your cluster using your favorite programming language.
Choose your language
Choose the language you want to use to build your application.
The Java application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the topology-aware Yugabyte JDBC driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in Java.
The application requires the following:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.8, or later, is installed. JDK installers for Linux and macOS can be downloaded from Oracle, Adoptium (OpenJDK), or Azul Systems (OpenJDK). Homebrew users on macOS can install using
brew install openjdk. - Apache Maven 3.3 or later.
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-java-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-java-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
app.propertiesfile located in the applicationsrc/main/resources/folder. -
Set the following configuration parameters:
- host - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- port - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- database - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - dbUser and dbPassword - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- sslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
verify-full. - sslRootCert - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- sslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Build the application.
$ mvn clean package -
Start the application.
$ java -cp target/yugabyte-simple-java-app-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar SampleApp
If you are running the application on a free or single node cluster, the driver displays a warning that the load balance failed and will fall back to a regular connection.
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created DemoAccount table.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic Java application that works with YugabyteDB.
The Go application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the Go PostgreSQL driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in Go.
The application requires the following:
- Go (tested with version 1.17.6).
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-go-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-go-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.gofile. -
Set the following configuration parameter constants:
- host - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- port - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- dbName - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - dbUser and dbPassword - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- sslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
verify-full. - sslRootCert - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- sslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Initialize the
GO111MODULEvariable.$ export GO111MODULE=auto -
Import the Go PostgreSQL driver.
$ go get github.com/lib/pq -
Start the application.
$ go run sample-app.go
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic Go application that works with YugabyteDB.
The Python application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the Python psycopg2 PostgreSQL database adapter and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in Python.
The application requires the following:
- Python 3.6 or later (Python 3.9.7 or later if running macOS on Apple silicon).
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-python-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-python-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.pyfile. -
Set the following configuration parameter constants:
- host - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- port - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- dbName - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - dbUser and dbPassword - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- sslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
verify-full. - sslRootCert - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- sslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Install psycopg2 PostgreSQL database adapter.
$ pip3 install psycopg2-binary -
Start the application.
$ python3 sample-app.py
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic Python application that works with YugabyteDB.
The Node.js application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the node-postgres driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in Node.js.
The application requires the following:
- The latest version of Node.js.
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-node-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-node-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.jsfile. -
Set the following configuration parameter constants:
- host - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- port - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- database - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - user and password - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- ssl - To enable
verify-caSSL mode, therejectUnauthorizedproperty is set totrueto require root certificate chain validation; replacepath_to_your_root_certificatewith the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- ssl - To enable
-
Save the file.
-
-
Install the node-postgres module.
npm install pg -
Install the async utility:
npm install --save async -
Start the application.
$ node sample-app.js
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic Node.js application that works with YugabyteDB.
The C application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the libpq driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in C.
The application requires the following:
- 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) architecture machine. (Use Rosetta to build and run on Apple silicon.)
- gcc 4.1.2 or later, or clang 3.4 or later installed.
- OpenSSL 1.1.1 or later (used by libpq to establish secure SSL connections).
- libpq. Homebrew users on macOS can install using
brew install libpq. You can download the PostgreSQL binaries and source from PostgreSQL Downloads.
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-c-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-c-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.cfile. -
Set the following configuration-related macros:
- HOST - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- PORT - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- DB_NAME - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - USER and PASSWORD - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
verify-full. - SSL_ROOT_CERT - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Build the application with gcc or clang.
gcc sample-app.c -o sample-app -I<path-to-libpq>/libpq/include -L<path-to-libpq>/libpq/lib -lpq -
Replace
<path-to-libpq>with the path to the libpq installation; for example,/usr/local/opt. -
Start the application.
$ ./sample-app
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic C application that works with YugabyteDB.
The C++ application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the libpqxx driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in C++.
The application requires the following:
- 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) architecture machine. (Use Rosetta to build and run on Apple silicon.)
- gcc 4.1.2 or later, or clang 3.4 or later installed.
- OpenSSL 1.1.1 or later (used by libpq and libpqxx to establish secure SSL connections).
- libpq. Homebrew users on macOS can install using
brew install libpq. You can download the PostgreSQL binaries and source from PostgreSQL Downloads. - libpqxx. Homebrew users on macOS can install using
brew install libpqxx. To build the driver yourself, refer to Building libpqxx.
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-cpp-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-cpp-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.cppfile. -
Set the following configuration-related constants:
- HOST - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- PORT - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- DB_NAME - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - USER and PASSWORD - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
verify-full. - SSL_ROOT_CERT - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Build the application with gcc or clang.
g++ -std=c++17 sample-app.cpp -o sample-app -lpqxx -lpq \ -I<path-to-libpq>/libpq/include -I<path-to-libpqxx>/libpqxx/include \ -L<path-to-libpq>/libpq/lib -L<path-to-libpqxx>/libpqxx/lib -
Replace
<path-to-libpq>with the path to the libpq installation, and<path-to-libpqxx>with the path to the libpqxx installation; for example,/usr/local/opt. -
Start the application.
$ ./sample-app
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic C++ application that works with YugabyteDB.
The C# application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the Npgsql driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in C#.
The application requires the following:
- .NET 6.0 SDK or later.
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-csharp-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-csharp-appThe
yugabyte-simple-csharp-app.csprojfile includes the following package reference to include the driver:<PackageReference Include="npgsql" Version="6.0.3" /> -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.csfile. -
Set the following configuration-related parameters:
- urlBuilder.Host - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- urlBuilder.Port - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- urlBuilder.Database - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - urlBuilder.Username and urlBuilder.Password - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- urlBuilder.SslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
SslMode.VerifyFull. - urlBuilder.RootCertificate - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- urlBuilder.SslMode - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Build and run the application.
dotnet run
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic C# application that works with YugabyteDB.
The Ruby application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the Ruby Pg driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in Ruby.
The application requires the following:
-
Ruby 3.1 or later.
-
OpenSSL 1.1.1 or later (used by libpq and pg to establish secure SSL connections).
-
libpq. Homebrew users on macOS can install using
brew install libpq. You can download the PostgreSQL binaries and source from PostgreSQL Downloads. -
Ruby pg. To install Ruby pg, run the following command:
gem install pg -- --with-pg-include=<path-to-libpq>/libpq/include --with-pg-lib=<path-to-libpq>/libpq/libReplace
<path-to-libpq>with the path to the libpq installation; for example,/usr/local/opt.
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-ruby-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-ruby-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.rbfile. -
Set the following configuration-related parameters:
- host - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- port - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- dbname - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - user and password - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- sslmode - the SSL mode to use; use
verify-full. - sslrootcert - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- sslmode - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Make the application file executable.
chmod +x sample-app.rb -
Run the application.
$ ./sample-app.rb
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic Ruby application that works with YugabyteDB.
The Rust application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the Rust-Postgres driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in Rust.
The application requires the following:
- Rust development environment. The sample application was created for Rust 1.58 but should work for earlier and later versions.
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-rust-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-rust-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.rsfile in thesrcdirectory. -
Set the following configuration-related constants:
- HOST - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- PORT - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- DB_NAME - the name of the database you are connecting to (the default is
yugabyte). - USER and PASSWORD - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
SslMode::Require. - SSL_ROOT_CERT - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Build and run the application.
$ cargo run
The driver is included in the dependencies list of the Cargo.toml file and installed automatically the first time you run the application.
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic Rust application that works with YugabyteDB.
The PHP application connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the php-pgsql driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB in PHP.
The application requires the following:
- PHP runtime. The sample application was created using PHP 8.1 but should work with earlier and later versions. Homebrew users on macOS can install PHP using
brew install php. - php-pgsql driver.
- On macOS, Homebrew automatically installs the driver with
brew install php. - Ubuntu users can install the driver using the
sudo apt-get install php-pgsqlcommand. - CentOS users can install the driver using the
sudo yum install php-pgsqlcommand.
- On macOS, Homebrew automatically installs the driver with
To build and run the application, do the following:
-
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/YugabyteDB-Samples/yugabyte-simple-php-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-php-app -
Provide connection parameters.
(You can skip this step and use the defaults if your cluster is running locally and listening on 127.0.0.1:5433.)
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
sample-app.phpfile. -
Set the following configuration-related constants:
- HOST - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. For local clusters, use the default (127.0.0.1). For YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Connection Parameters.
- PORT - the port number for the driver to use (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- DB_NAME - the name of the database to connect to (the default is
yugabyte). - USER and PASSWORD - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. For local clusters, use the defaults (
yugabyte). For YugabyteDB Managed, use the credentials in the credentials file you downloaded.
-
YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections, so you need to set the following additional parameters:
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
verify-full. - SSL_ROOT_CERT - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
- SSL_MODE - the SSL mode to use; use
-
Save the file.
-
-
Run the application.
$ php sample-app.php
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created table DemoAccount.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic PHP application that works with YugabyteDB.