Alerts
Use alerts to notify you and your team members when cluster and database resource usage exceeds predefined limits, or of potential billing issues.
You configure alerts and notifications on the Alerts page.
To monitor clusters in real time, use the performance metrics on the cluster Overview and Performance tabs.
Features
- YugabyteDB Managed sends email notifications to all account members.
- When an alert triggers, YugabyteDB Managed sends an email notification once, regardless of how long the condition lasts.
- When an alert triggers, a notification displays on the Notifications page. After the alert condition resolves, the notification dismisses automatically.
- Alerts are enabled for all clusters in your account.
- Alerts can have two severity levels: Warning or Severe. A third level, Info, does not trigger a notification.
Configure alerts
Enable alerts using the Configurations tab on the Alerts page.
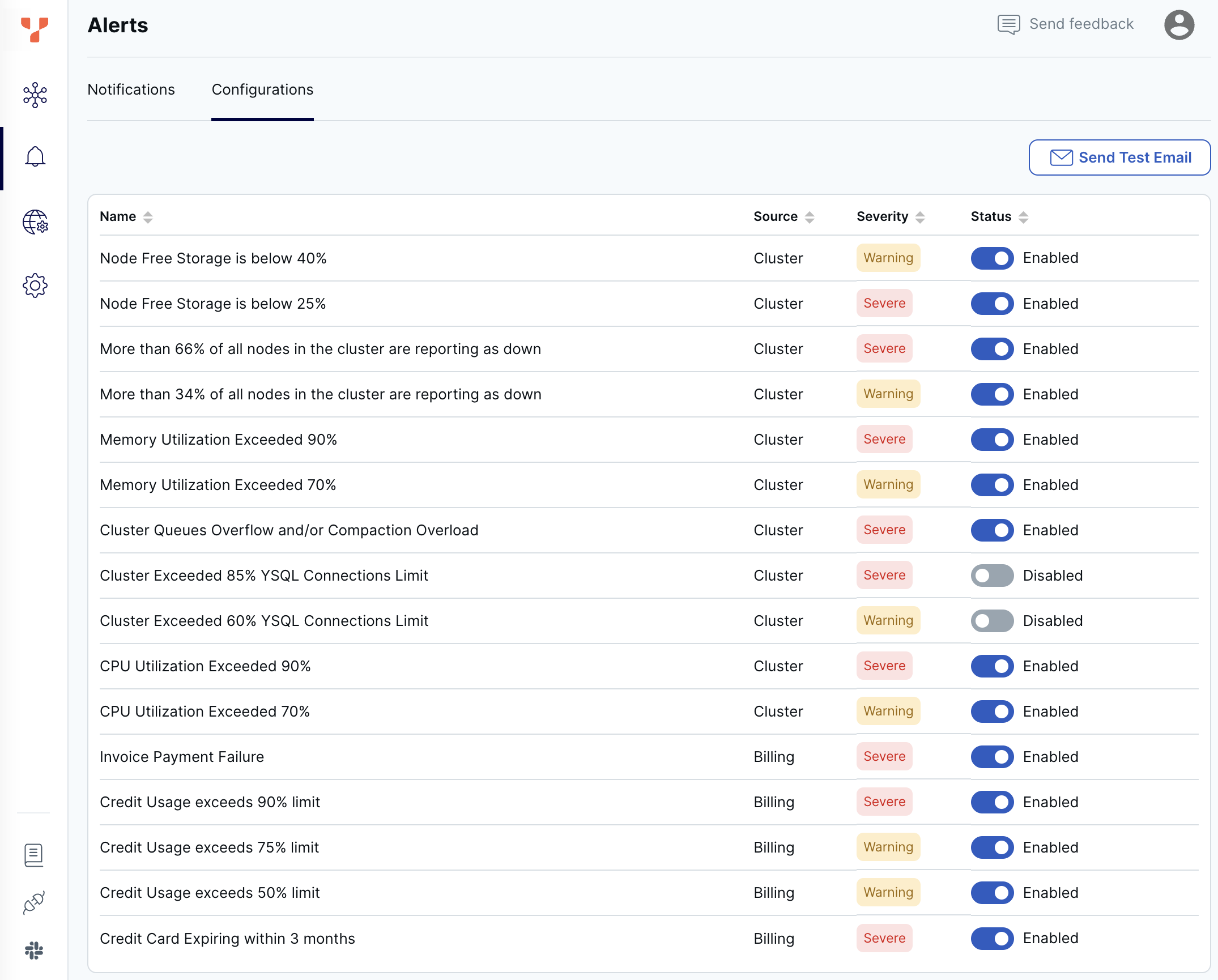
To change an alert, click the toggle in the Status column.
To test that you can receive email from the Yugabyte server, click Send Test Email.
Review notifications
Open notifications are listed on the Notifications tab on the Alerts page.
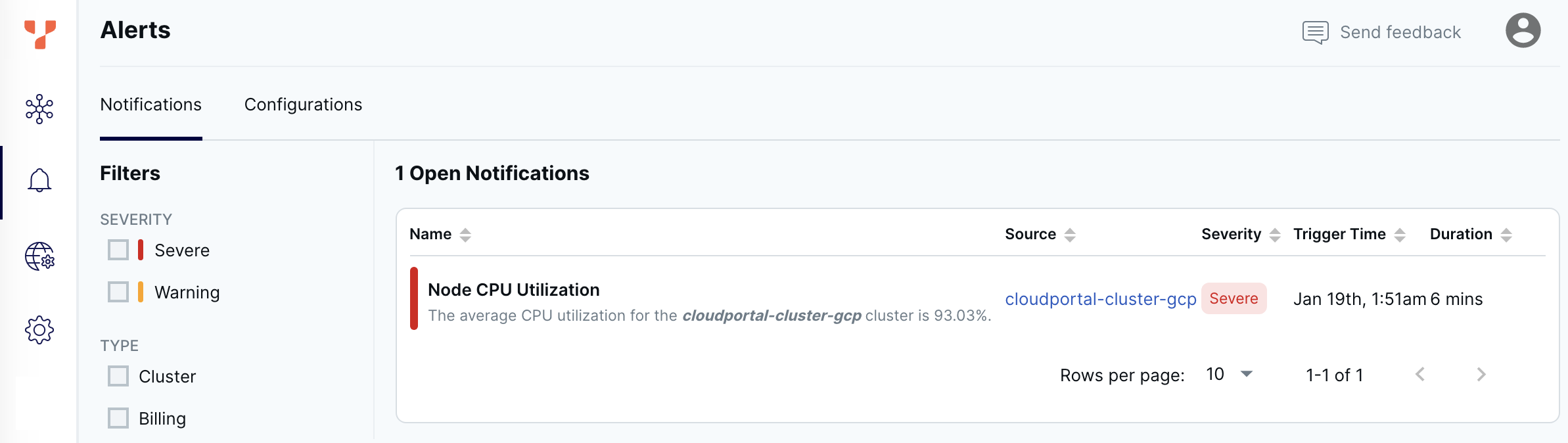
When the condition that caused the alert resolves, the notification dismisses automatically.
Cluster health
YugabyteDB monitors the health of your clusters based on cluster alert conditions and displays the health as either Healthy, Needs Attention, or Unhealthy. The following table provides details on the criteria used to determine the cluster health.
| Status | Alert | Level |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy | No alerts Fewer than 34% of nodes down |
Info |
| Needs Attention | Node free storage More than 34% of nodes down Memory Utilization YSQL Connections CPU Utilization |
Warning or Severe Warning Warning or Severe Warning or Severe Warning or Severe |
| Unhealthy | More than 66% of nodes down | Severe |
To see the alert conditions that caused the current health condition, click the cluster health icon.
If multiple alerts are triggered, the most severe alert determines the health that is reported.
Cluster health is updated every three minutes.
Fixing alerts
Alerts can trigger for issues with a particular cluster, or for billing issues.
Alerts can have two severity levels: Warning or Severe. The nodes down alert has a third level, Info, which is reported in the cluster health, and does not trigger a notification.
Cluster alerts
When you receive a cluster alert, the first step is to review the chart for the metric over time to evaluate trends and monitor your progress. The following charts are available:
| Alert | Chart |
|---|---|
| Node Free Storage | Disk Usage |
| Memory Use | Memory Usage |
| Cluster Queues Overflow | RPC Queue Size |
| Compaction Overload | Compaction |
| YSQL Connections | YSQL Operations/Sec |
| CPU Utilization | CPU Usage |
For a nodes down alert, go to the cluster Nodes tab to see which nodes are down.
You can view the metrics on the cluster Performance tab. Refer to Performance metrics.
Note
If you get frequent cluster alerts on a Sandbox cluster, you may have reached the performance limits for Sandbox clusters. Consider upgrading to a Dedicated cluster.Fix storage alerts
YugabyteDB Managed sends a notification when the free storage on any node in the cluster falls below the threshold, as follows:
- Node free storage is below 40% (Warning).
- Node free storage is below 25% (Severe).
Once disk capacity falls below 25% for any node, look at your database for unused tables that you can truncate or drop.
Consider increasing the disk space per node. By default, you are entitled to 50GB per vCPU. Adding vCPUs also automatically increases disk space.
For information on scaling clusters, refer to Scale and configure clusters.
Fix nodes reporting as down alerts
YugabyteDB Managed sends a notification when the number of nodes that are down in a cluster exceeds the threshold, as follows:
- More than 34% of all nodes in the cluster are reporting as down (Warning).
- More than 66% of all nodes in the cluster are reporting as down (Severe).
If fewer than 34% of nodes in a multi-node (that is, highly available) cluster are down, the cluster remains healthy and can continue to serve requests, and the status is reported in the cluster health.
If more than 66% of nodes in a multi-node (that is, highly available) cluster are down, the cluster is considered unhealthy and the downed nodes should be replaced as soon as possible.
When cluster nodes go down, Yugabyte is notified automatically and will restore the nodes as quickly as possible.
Fix memory alerts
YugabyteDB Managed sends a notification when memory use in the cluster exceeds the threshold, as follows:
- Memory use exceeds 75% (Warning).
- Memory use exceeds 90% (Severe).
If your cluster experiences frequent spikes in memory use, consider optimizing your workload.
Unoptimized queries can lead to memory alerts. Use the Slow Queries and Live Queries views to identify potentially problematic queries, then use the EXPLAIN statement to see the query execution plan and identify optimizations. Consider adding one or more indexes to improve query performance. For more information, refer to Analyzing Queries with EXPLAIN.
If memory use is continuously higher than 80%, your workload may also exceed the capacity of your cluster. If the issue isn't a single query that consumes a lot of memory on a single tablet, consider scaling your cluster vertically by adding vCPUs to increase capacity per node, or horizontally by adding nodes to reduce the load per node. Refer to Scale and configure clusters.
High memory use could also indicate a problem and may require debugging by Yugabyte Support.
Fix database overload alerts
YugabyteDB Managed sends the following database overload alert:
- Cluster queues overflow and/or compaction overload.
This alert triggers if any one of the following conditions occurs:
- The number of client requests that timed out waiting in the service queue is greater than 0 for 10 minutes. This can be caused by your application generating requests (such as queries and scans) at a rate faster than the database can process them.
- The number of client requests dropped because the service queue was full is greater than 0 for 10 minutes. This can be caused by your application generating requests (such as queries and scans) at a rate faster than the database can process them.
- The number of rejected compaction requests is greater than 0 for 10 minutes. This can be caused by running a high INSERT/ UPDATE/ DELETE workload on a cluster that is undersized.
Cluster queue overflow and compaction overload are indicators of the incoming traffic and system load. If the backends get overloaded, requests pile up in the queues. When the queue is full, the system responds with backpressure errors. This can cause performance degradation.
If your cluster generates this alert, you may need to rate limit your queries. Look at optimizing the application generating the requests in the following ways:
- Examine the application retry logic, and reduce total retry count.
- Increase client request timeout at the driver layer.
- Reduce query parallelism.
- If needed, set the driver execution to "sync" rather than "async" to serialize queries.
If your cluster generates this alert but isn't under a very large workload, contact Yugabyte Support.
Fix YSQL connection alerts
YugabyteDB Managed clusters support 10 simultaneous connections per vCPU. YugabyteDB Managed sends a notification when the number of YSQL connections on any node in the cluster exceeds the threshold, as follows:
- YSQL connections exceeds 60% of the limit (Warning).
- YSQL connections exceeds 95% of the limit (Severe).
If your cluster experiences frequent spikes in connections, consider optimizing your application's connection code.
If connections are opened but never closed, your application will eventually exceed the connection limit.
You may need to implement some form of connection pooling.
If the number of connections is continuously higher than 60%, your workload may also exceed the capacity of your cluster. Be sure to size your cluster with enough spare capacity to remain fault tolerant during maintenance events and outages. For example, during an outage or a rolling restart for maintenance, a 3 node cluster loses a third of its capacity. The remaining nodes need to be able to handle the traffic from the absent node.
To add connection capacity, scale your cluster by adding vCPUs or nodes. Refer to Scale and configure clusters.
Fix CPU alerts
YugabyteDB Managed sends a notification when CPU use on any node in the cluster exceeds the threshold, as follows:
- Node CPU use exceeds 70% on average for at least 5 minutes (Warning).
- Node CPU use exceeds 90% on average for at least 5 minutes (Severe).
If your cluster experiences frequent spikes in CPU use, consider optimizing your workload.
Unoptimized queries can lead to CPU alerts. Use the Slow Queries and Live Queries views to identify potentially problematic queries, then use the EXPLAIN statement to see the query execution plan and identify optimizations. Consider adding one or more indexes to improve query performance. For more information, refer to Analyzing Queries with EXPLAIN.
High CPU use could also indicate a problem and may require debugging by Yugabyte Support.
If CPU use is continuously higher than 80%, your workload may also exceed the capacity of your cluster. Consider scaling your cluster vertically by adding vCPUs to increase capacity per node, or horizontally by adding nodes to reduce the load per node. Refer to Scale and configure clusters.
Billing alerts
Billing alerts trigger for the following events:
| Alert | Response |
|---|---|
| Invoice payment failure | Check with your card issuer to ensure that your card is still valid and has not exceeded its limit. Alternatively, you can add another credit card to your billing profile. |
| Credit usage exceeds the 50%, 75%, and 90% limit | Add a credit card to your billing profile, or contact Yugabyte Support. |
| Credit card expiring within 3 months | Add a new credit card. |
For information on adding credit cards and managing your billing profile, refer to Manage your billing profile and payment method.