Create provider configuration
Before you can deploy universes using YugabyteDB Anywhere, you must create a provider configuration. Create a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provider configuration if your target cloud is GCP.
A provider configuration describes your cloud environment (such as its service account, regions and availability zones, NTP server, certificates that may be used to SSH to VMs, the Linux disk image to be used for configuring the nodes, and so on). The provider configuration is used as an input when deploying a universe, and can be reused for many universes.
When deploying a universe, YugabyteDB Anywhere uses the provider configuration settings to do the following:
-
Create instances on GCP using the following:
- your cloud provider credentials
- specified regions and availability zones (this can be a subset of those specified in the provider configuration)
- a Linux image
-
Provision those VMs with YugabyteDB software.
Note: YugabyteDB Anywhere needs network connectivity to the VMs, service account for the provisioning step above, and for subsequent management, as described in Cloud prerequisites.
Prerequisites
- Cloud provider credentials. YugabyteDB Anywhere uses your credentials to automatically provision and de-provision instances that run YugabyteDB. An instance for YugabyteDB includes a compute instance, as well as local or remote disk storage attached to the compute instance.
Configure GCP
Navigate to Configs > Infrastructure > Google Cloud Platform to see a list of all currently configured GCP providers.
View and edit providers
To view a provider, select it in the list of GCP Configs to display the Overview.
To edit the provider, select Config Details, make changes, and click Apply Changes. For more information, refer to Provider settings. Note that, depending on whether the provider has been used to create a universe, you can only edit a subset of options.
To view the universes created using the provider, select Universes.
To delete the provider, click Actions and choose Delete Configuration. You can only delete providers that are not in use by a universe.
Create a provider
To create a GCP provider:
-
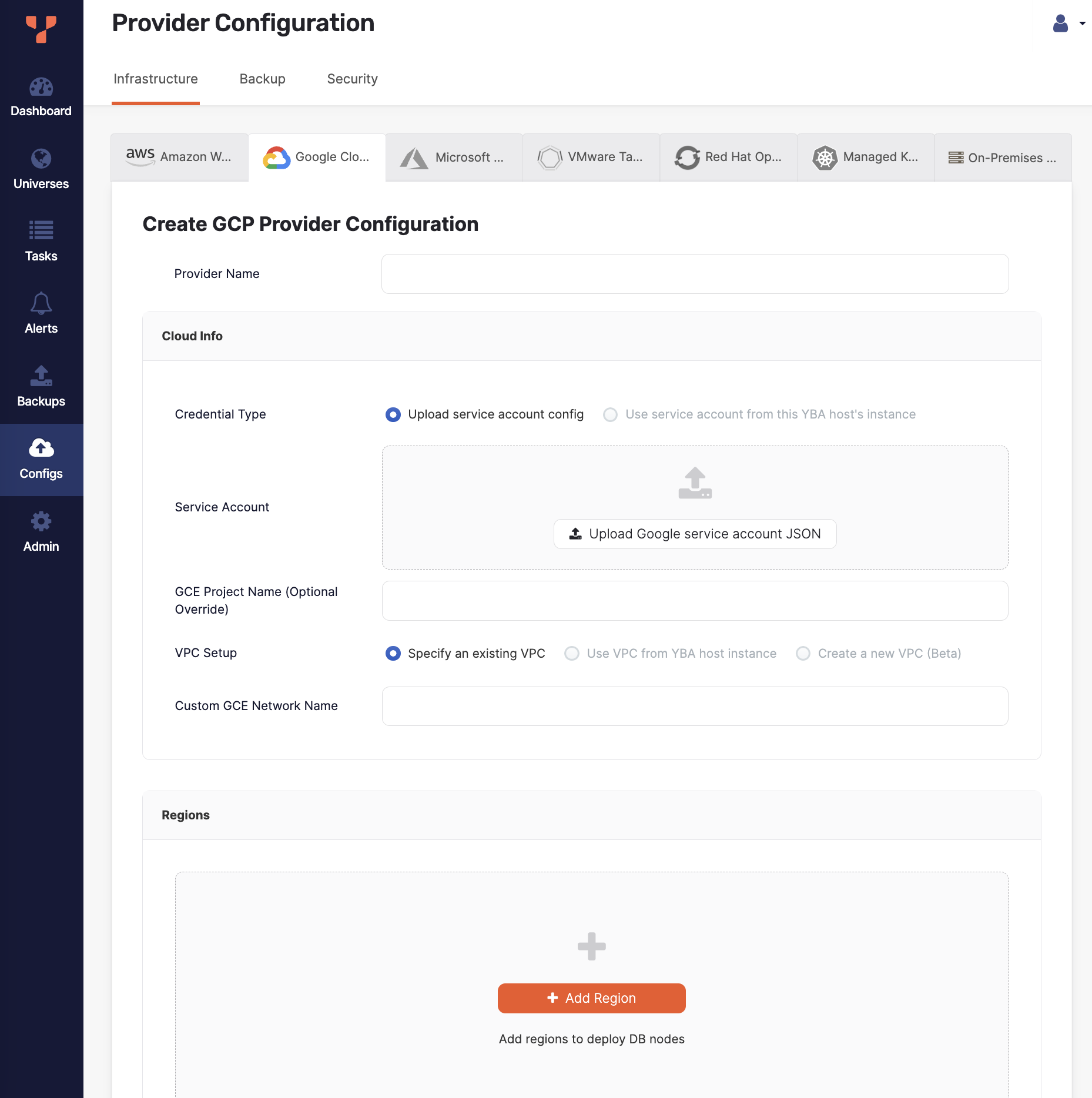
Click Create Config to open the Create GCP Provider Configuration page.
-
Enter the provider details. Refer to Provider settings.
-
Click Create Provider Configuration when you are done and wait for the configuration to complete.
This process includes generating a new VPC, a network, subnetworks in all available regions, as well as a new firewall rule, VPC peering for network connectivity, and a custom SSH key pair for YugabyteDB Anywhere-to-YugabyteDB connectivity.
Now you are ready to create a YugabyteDB universe on GCP.
Provider settings
Provider Name
Enter a Provider name. The Provider name is an internal tag used for organizing provider configurations.
Cloud Info
If your YugabyteDB Anywhere instance is not running inside GCP, you need to supply YugabyteDB Anywhere with credentials to the desired GCP project by uploading a configuration file. To do this, set Credential Type to Upload Service Account config and proceed to upload the JSON file that you obtained when you created your service account, as described in Prepare the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) environment.
If your YugabyteDB Anywhere instance is running inside GCP, the preferred method for authentication to the GCP APIs is to add a service account role to the GCP instance running YugabyteDB Anywhere and then configure YugabyteDB Anywhere to use the instance's service account. To do this, set Credential Type to Use service account from this YBA host's instance.
VPC Setup
Specify the VPC to use for deploying YugabyteDB nodes.
You may choose one of the following options:
-
Specify an existing VPC. Select this option to use a VPC that you have created in Google Cloud, and enter the Custom GCE Network Name of the VPC.
-
Use VPC from YBA host instance. If your YugabyteDB Anywhere host machine is also running on Google Cloud, you can use the same VPC on which the YugabyteDB Anywhere host machine runs. Credential Type must be set to Use service account from this YBA host's instance to use this option.
Note that choosing to use the same VPC as YugabyteDB Anywhere is an advanced option, which assumes that you are in complete control of this VPC and will be responsible for setting up the networking, SSH access, and firewall rules for it.
-
Create a new VPC. Select this option to create a new VPC using YugabyteDB Anywhere. This option is considered beta and, therefore, not recommended for production use cases. If there are any classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) conflicts, using this option can result in a silent failure. For example, the following will fail:
- Configure more than one GCP cloud provider with different CIDR block prefixes and selecting the Create a new VPC option.
- Creating a new VPC with a CIDR block that overlaps with any of the existing subnets.
To use this option, contact Yugabyte Support.
Regions
For each region that you want to use for this configuration, do the following:
- Click Add Region.
- Select the region.
- Optionally, specify a Custom Machine Image. YugabyteDB Anywhere allows you to bring up universes on Ubuntu 18.04 host nodes, assuming you have Python 2 or later installed on the host, as well as the provider created with a custom AMI and custom SSH user.
- Enter the ID of a shared subnet.
Advanced
You can customize the Network Time Protocol server, as follows:
-
Select Use GCP's NTP Server to enable cluster nodes to connect to the GCP internal time servers. For more information, consult the GCP documentation such as Configure NTP on a VM.
-
Select Specify Custom NTP Server(s) to provide your own NTP servers and allow the cluster nodes to connect to those NTP servers.
-
Select Assume NTP server configured in machine image to prevent YugabyteDB Anywhere from performing any NTP configuration on the cluster nodes. For data consistency, you will be responsible for manually configuring NTP.
Important
Use this option with caution. Time synchronization is critical to database data consistency; failure to run NTP may cause data loss.