Create provider configuration
Before you can deploy universes using YugabyteDB Anywhere, you must create a provider configuration.
A provider configuration describes your cloud environment (such as its regions and availability zones, NTP server, certificates that may be used to SSH to VMs, whether YugabyteDB database software will be manually installed by the user or auto-provisioned by YugabyteDB Anywhere, and so on). The provider configuration is used as an input when deploying a universe, and can be reused for many universes.
With on-premises providers, VMs are not auto-created by YugabyteDB Anywhere; you must manually create and add them to the free pool of the on-premises provider. Only after VM instances are added can YugabyteDB Anywhere auto-provision or can you manually provision the YugabyteDB database software and create universes from these database nodes.
Configure the on-premises provider
Navigate to Configs > Infrastructure > On-Premises Datacenters to see a list of all currently configured on-premises providers.
View and edit providers
To view a provider, select it in the list of On Prem Configs to display the Overview.
To edit the provider, select Config Details, make changes, and click Apply Changes. For more information, refer to Provider settings. Note that, depending on whether the provider has been used to create a universe, you can only edit a subset of options.
To view the universes created using the provider, select Universes.
To delete the provider, click Actions and choose Delete Configuration. You can only delete providers that are not in use by a universe.
Create a provider
To create an on-premises provider:
-
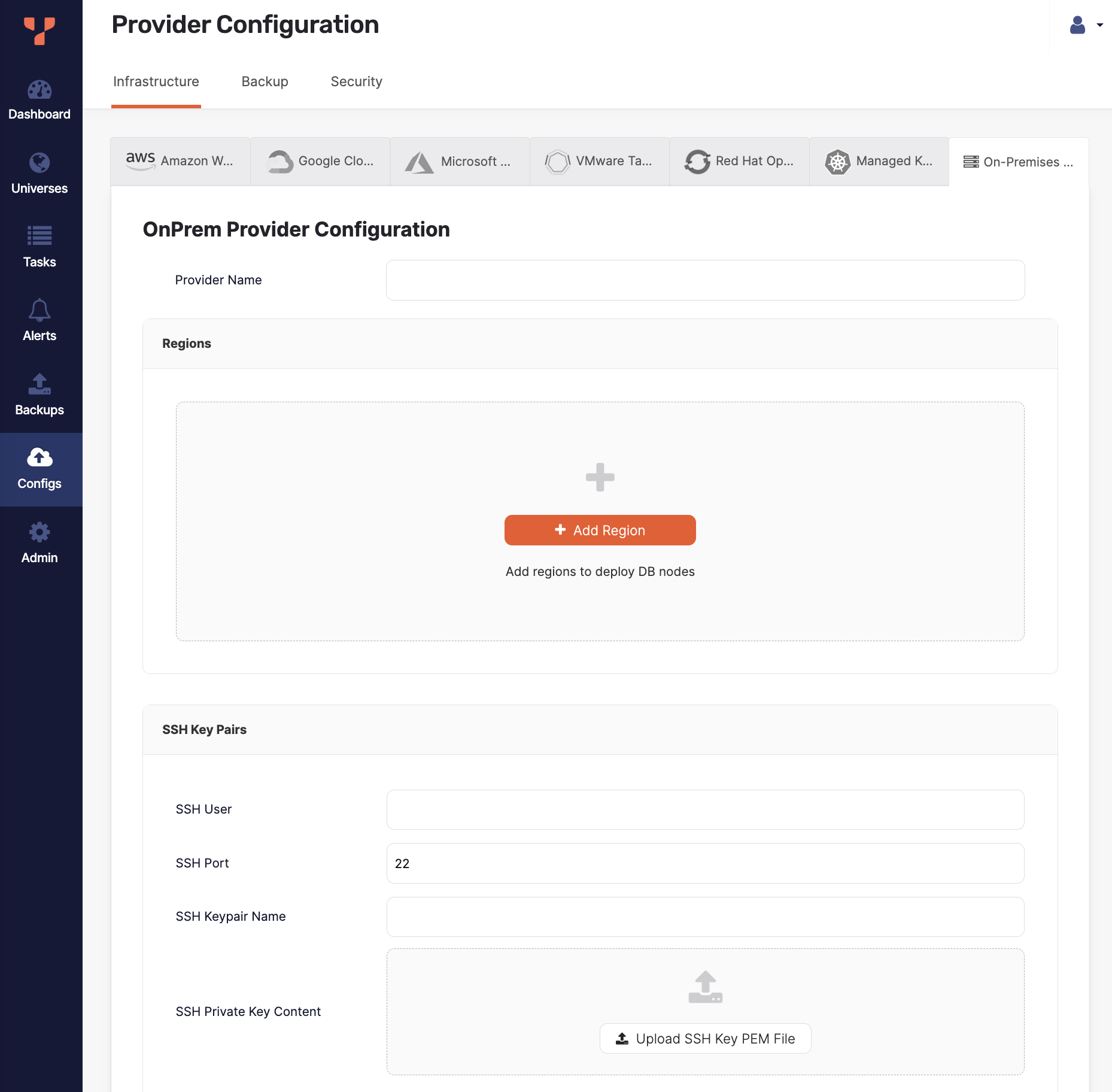
Click Create Config to open the OnPrem Provider Configuration page.
-
Enter the provider details. Refer to Provider settings.
-
Click Create Provider Configuration when you are done and wait for the configuration to complete.
Provider settings
Provider Name
Enter a Provider name. The Provider name is an internal tag used for organizing cloud providers.
Regions
To add regions for the provider, do the following:
-
Click Add Region.
-
Enter a name for the region.
-
Select the region location.
-
To add a zone, click Add Zone and enter a name for the zone.
-
Click Add Region.
SSH Key Pairs
In the SSH User field, enter the name of the user that has SSH privileges on your instances. This is required because to provision on-premises nodes with YugabyteDB, YugabyteDB Anywhere needs SSH access to these nodes. Unless you plan to provision the database nodes manually, the user needs to have password-free sudo permissions to complete a few tasks.
If the SSH user requires a password for sudo access or the SSH user does not have sudo access, follow the steps described in Provision nodes manually.
In the SSH Port field, provide the port number of SSH client connections.
Use the SSH Private Key Content field to upload the private key PEM file available to the SSH user for gaining access via SSH into your instances.
Advanced
Disable the DB Nodes have public internet access option if you want the installation to run in an air-gapped mode without expecting any internet access.
Enable the Manually Provision Nodes field if you choose to manually set up your database nodes. Otherwise, YugabyteDB Anywhere will use the sudo user to set up YugabyteDB nodes. For manual provisioning, you would be prompted to run a Python script at a later stage or to run a set of commands on the database nodes.
If any of the following statements are applicable to your use case, you need to provision the nodes manually:
- Preprovisioned
yugabyte:yugabyteuser and group. - Sudo user requires a password.
- The SSH user is not a sudo user.
Optionally, use the YB Nodes Home Directory field to specify the home directory of the yugabyte user. The default value is /home/yugabyte.
Enable Install Node Exporter if you want the node exporter installed. You can skip this step if you have node exporter already installed on the nodes. Ensure you have provided the correct port number for skipping the installation.
The Node Exporter User field allows you to override the default prometheus user. This is helpful when the user is preprovisioned on nodes (when the user creation is disabled). If overridden, the installer checks whether or not the user exists and creates the user if it does not exist.
Use the Node Exporter Port field to specify the port number for the node exporter. The default value is 9300.
NTP Setup lets you to customize the Network Time Protocol server, as follows:
- Select Manually add NTP Servers to provide your own NTP servers and allow the cluster nodes to connect to those NTP servers.
- Select Don't set up NTP to prevent YugabyteDB Anywhere from performing any NTP configuration on the cluster nodes. For data consistency, ensure that NTP is correctly configured on your machine image.
Configure hardware for YugabyteDB nodes
After the provider has been created, you can configure the hardware for the configuration by navigating to Configs > Infrastructure > On-Premises Datacenters, selecting the On Prem Config you created, and choosing Instances. This displays the configured instance types and instances for the selected provider.
Add instance types
To add an instance type, do the following:
-
Click Add Instance Type.
-
Complete the Add Instance Type dialog fields, as follows:
- Use the Machine Type field to define a value to be used internally as an identifier in the Instance Type universe field.
- Use the Number of Cores field to define the number of cores to be assigned to a node.
- Use the Memory Size (GB) field to define the memory allocation of a node.
- Use the Volume Size (GB) field to define the disk volume of a node.
- Use the Mount Paths field to define a mount point with enough space to contain your node density. Use
/data. If you have multiple drives, add these as a comma-separated list, such as, for example,/mnt/d0,/mnt/d1.
-
Click Add Instance Type.
Add YugabyteDB nodes
For each node you want to add, click Add Instances to add a YugabyteDB node. For each region, select the zone and instance type. You can use DNS names or IP addresses when adding instances (instance ID is an optional user-defined identifier).
Click Add to add additional nodes in the region.
Note that if you provide a hostname, the universe might experience issues communicating. To resolve this, you need to delete the failed universe and then recreate it with the use_node_hostname_for_local_tserver flag enabled.
Provision nodes manually
To provision your nodes manually, you have the following two options:
- If the SSH user you provided has sudo privileges but requires a password, you can run the preprovisioning script.
- If the SSH user does not have any sudo privileges, you need to set up the database nodes manually.
Run the preprovisioning script
This step is only required if you set Manually Provision Nodes to true and the SSH user has sudo privileges which require a password; otherwise you skip this step.
You can manually provision each node using the preprovisioning Python script, as follows:
-
Login to YugabyteDB Anywhere virtual machine via SSH.
-
Access the Docker
yugawarecontainer, as follows:sudo docker exec -it yugaware bash -
Copy and paste the Python script prompted via the UI and substitute for a node IP address and mount points. Optionally, use the
--ask_passwordflag if the sudo user requires password authentication, as follows:/opt/yugabyte/yugaware/data/provision/9cf26f3b-4c7c-451a-880d-593f2f76efce/provision_instance.py --ip 10.9.116.65 --mount_points /data --ask_passwordExpect the following output and prompt:
Executing provision now for instance with IP 10.9.116.65... SUDO password: -
Wait for the script to finish successfully.
-
Repeat step 3 for every node that will participate in the universe.
This completes the on-premises cloud provider configuration. You can proceed to Configure the backup target or Create deployments.
Set up database nodes manually
This step is only required if you set Manually Provision Nodes to true and the SSH user does not have sudo privileges at all; otherwise you skip this step.
If the SSH user configured in the on-premises provider does not have sudo privileges, then you can set up each of the database nodes manually. Note that you need access to a user with sudo privileges in order to complete these steps.
For each node, perform the following:
- Set up time synchronization
- Open incoming TCP ports
- Preprovision the node
- Install Prometheus node exporter
- Install backup utilities
- Set crontab permissions
- Install systemd-related database service unit files (optional)
Set up time synchronization
A local Network Time Protocol (NTP) server or equivalent must be available.
Ensure an NTP-compatible time service client is installed in the node OS (chrony is installed by default in the standard CentOS 7 instance used in this example). Then, configure the time service client to use the available time server. The procedure includes this step and assumes chrony is the installed client.
Open incoming TCP/IP ports
Database servers need incoming TCP/IP access enabled to the following ports, for communications between themselves and YugabyteDB Anywhere:
| Protocol | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 22 | SSH (for automatic administration) |
| TCP | 5433 | YSQL client |
| TCP | 6379 | YEDIS client |
| TCP | 7000 | YB master webserver |
| TCP | 7100 | YB master RPC |
| TCP | 9000 | YB tablet server webserver |
| TCP | 9042 | YCQL client |
| TCP | 9090 | Prometheus server |
| TCP | 9100 | YB tablet server RPC |
| TCP | 9300 | Prometheus node exporter |
| TCP | 12000 | YCQL HTTP (for DB statistics gathering) |
| TCP | 13000 | YSQL HTTP (for DB statistics gathering) |
| TCP | 18018 | YB Controller |
The preceding table is based on the information on the default ports page.
Preprovision nodes manually
This process carries out all provisioning tasks on the database nodes which require elevated privileges. After the database nodes have been prepared in this way, the universe creation process from YugabyteDB Anywhere will connect with the nodes only via the yugabyte user, and not require any elevation of privileges to deploy and operate the YugabyteDB universe.
Physical nodes (or cloud instances) are installed with a standard CentOS 7 server image. The following steps are to be performed on each physical node, prior to universe creation:
-
Login to each database node as a user with sudo enabled (the
centosuser in centos7 images). -
Add the following line to the
/etc/chrony.conffile:server <your-time-server-IP-address> prefer iburstThen run the following command:
sudo chronyc makestep # (force instant sync to NTP server) -
Add a new
yugabyte:yugabyteuser and group with the default login shell/bin/bashthat you set via the-sflag, as follows:sudo useradd -s /bin/bash -m yugabyte # (add user yugabyte and create /home/yugabyte) sudo passwd yugabyte # (add a password to the yugabyte user) sudo su - yugabyte # (change to yugabyte user for execution of next steps)Ensure that the
yugabyteuser has permissions to SSH into the YugabyteDB nodes (as defined in/etc/ssh/sshd_config). -
Copy the SSH public key to each DB node. This public key should correspond to the private key entered into the YugabyteDB Anywhere provider.
-
Run the following commands as the
yugabyteuser, after copying the SSH public key file to the user home directory:cd ~yugabyte mkdir .ssh chmod 700 .ssh cat <pubkey file> >> .ssh/authorized_keys chmod 400 .ssh/authorized_keys exit # (exit from the yugabyte user back to previous user) -
Add the following lines to the
/etc/security/limits.conffile (sudo is required):* - core unlimited * - data unlimited * - fsize unlimited * - sigpending 119934 * - memlock 64 * - rss unlimited * - nofile 1048576 * - msgqueue 819200 * - stack 8192 * - cpu unlimited * - nproc 12000 * - locks unlimited -
Modify the following line in the
/etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conffile:* soft nproc 12000 -
Install the rsync and OpenSSL packages (if not already included with your Linux distribution) using the following commands:
sudo yum install openssl sudo yum install rsyncFor airgapped environments, make sure your Yum repository mirror contains these packages.
-
If running on a virtual machine, execute the following to tune kernel settings:
-
Configure the parameter
vm.swappinessas follows:sudo bash -c 'sysctl vm.swappiness=0 >> /etc/sysctl.conf' sudo sysctl kernel.core_pattern=/home/yugabyte/cores/core_%p_%t_%E >> /etc/sysctl.conf -
Configure the parameter
vm.max_map_countas follows:sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144 sudo bash -c 'sysctl vm.max_map_count=262144 >> /etc/sysctl.conf' -
Validate the change as follows:
sysctl vm.max_map_count
-
-
Perform the following to prepare and mount the data volume (separate partition for database data):
-
List the available storage volumes, as follows:
lsblk -
Perform the following steps for each available volume (all listed volumes other than the root volume):
sudo mkdir /data # (or /data1, /data2 etc) sudo mkfs -t xfs /dev/nvme1n1 # (create xfs filesystem over entire volume) sudo vi /etc/fstab -
Add the following line to
/etc/fstab:/dev/nvme1n1 /data xfs noatime 0 0 -
Exit from vi, and continue, as follows:
sudo mount -av # (mounts the new volume using the fstab entry, to validate) sudo chown yugabyte:yugabyte /data sudo chmod 755 /data
-
Install Prometheus node exporter
Download the 1.3.1 version of the Prometheus node exporter, as follows:
wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.3.1/node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
If you are doing an airgapped installation, download the node exporter using a computer connected to the internet and copy it over to the database nodes.
On each node, perform the following as a user with sudo access:
-
Copy the
node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64.gzpackage file that you downloaded into the/tmpdirectory on each of the YugabyteDB nodes. Ensure that this file is readable by the user (for example,centos). -
Run the following commands:
sudo mkdir /opt/prometheus sudo mkdir /etc/prometheus sudo mkdir /var/log/prometheus sudo mkdir /var/run/prometheus sudo mv /tmp/node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64.tar /opt/prometheus sudo adduser --shell /bin/bash prometheus # (also adds group "prometheus") sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /opt/prometheus sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /var/log/prometheus sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /var/run/prometheus sudo chmod +r /opt/prometheus/node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64.tar sudo su - prometheus (user session is now as user "prometheus") -
Run the following commands as user
prometheus:cd /opt/prometheus tar zxf node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz exit # (exit from prometheus user back to previous user) -
Edit the following file:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.serviceAdd the following to the
/etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.servicefile:[Unit] Description=node_exporter - Exporter for machine metrics. Documentation=https://github.com/William-Yeh/ansible-prometheus After=network.target [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target [Service] Type=simple User=prometheus Group=prometheus ExecStart=/opt/prometheus/node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64/node_exporter --web.listen-address=:9300 --collector.textfile.directory=/tmp/yugabyte/metrics -
Exit from vi, and continue, as follows:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable node_exporter sudo systemctl start node_exporter -
Check the status of the
node_exporterservice with the following command:sudo systemctl status node_exporter
Install backup utilities
YugabyteDB Anywhere supports backing up YugabyteDB to Amazon S3, Azure Storage, Google Cloud Storage, and Network File System (NFS). For more information, see Configure backup storage.
You can install the backup utility for the backup storage you plan to use, as follows:
-
NFS: Install rsync, which YugabyteDB Anywhere uses to perform NFS backups installed during one of the previous steps.
-
Amazon S3: Install s3cmd, on which YugabyteDB Anywhere relies to support copying backups to Amazon S3. You have the following installation options:
-
For a regular installation, execute the following:
sudo yum install s3cmd -
For an airgapped installation, copy
/opt/third-party/s3cmd-2.0.1.tar.gzfrom the YugabyteDB Anywhere node to the database node, and then extract it into the/usr/localdirectory on the database node, as follows:cd /usr/local sudo tar xvfz path-to-s3cmd-2.0.1.tar.gz sudo ln -s /usr/local/s3cmd-2.0.1/s3cmd /usr/local/bin/s3cmd
-
-
Azure Storage: Install azcopy using one of the following options:
-
Download
azcopy_linux_amd64_10.13.0.tar.gzusing the following command:wget https://azcopyvnext.azureedge.net/release20211027/azcopy_linux_amd64_10.13.0.tar.gz -
For airgapped installations, copy
/opt/third-party/azcopy_linux_amd64_10.13.0.tar.gzfrom the YugabyteDB Anywhere node, as follows:cd /usr/local sudo tar xfz path-to-azcopy_linux_amd64_10.13.0.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin azcopy_linux_amd64_10.13.0/azcopy --strip-components 1
-
-
Google Cloud Storage: Install gsutil using one of the following options:
-
Download
gsutil_4.60.tar.gzusing the following command:wget https://storage.googleapis.com/pub/gsutil_4.60.tar.gz -
For airgapped installations, copy
/opt/third-party/gsutil_4.60.tar.gzfrom the YugabyteDB Anywhere node, as follows:cd /usr/local sudo tar xvfz gsutil_4.60.tar.gz sudo ln -s /usr/local/gsutil/gsutil /usr/local/bin/gsutil
-
Set crontab permissions
YugabyteDB Anywhere supports performing YugabyteDB liveness checks, log file management, and core file management using cron jobs.
Note that sudo is required to set up this service.
If YugabyteDB Anywhere will be using cron jobs, ensure that the yugabyte user is allowed to run crontab:
- If you are using the
cron.allowfile to manage crontab access, add theyugabyteuser to this file. - If you are using the
cron.denyfile, remove theyugabyteuser from this file.
If you are not using either file, no changes are required.
You have finished configuring your on-premises cloud provider. Proceed to Configure the backup target or Create deployments.
Install systemd-related database service unit files
As an alternative to setting crontab permissions, you can install systemd-specific database service unit files, as follows:
-
Enable the
yugabyteuser to run the following commands as sudo or root:yugabyte ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: /bin/systemctl start yb-master, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-master, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-master, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-master, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-master, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-tserver, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-tserver, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-tserver, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-tserver, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-tserver, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-controller, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-controller, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-controller, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-controller, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-controller, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-bind_check.service, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-bind_check.service, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-bind_check.service, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-bind_check.service, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-bind_check.service, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.timer, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.timer, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.timer, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.timer, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.timer, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-clean_cores.timer, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-clean_cores.timer, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-clean_cores.timer, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-clean_cores.timer, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-clean_cores.timer, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-collect_metrics.timer, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-collect_metrics.timer, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-collect_metrics.timer, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-collect_metrics.timer, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-collect_metrics.timer, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-zip_purge_yb_logs, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-zip_purge_yb_logs, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-zip_purge_yb_logs, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-zip_purge_yb_logs, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-zip_purge_yb_logs, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-clean_cores, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-clean_cores, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-clean_cores, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-clean_cores, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-clean_cores, \ /bin/systemctl start yb-collect_metrics, \ /bin/systemctl stop yb-collect_metrics, \ /bin/systemctl restart yb-collect_metrics, \ /bin/systemctl enable yb-collect_metrics, \ /bin/systemctl disable yb-collect_metrics, \ /bin/systemctl daemon-reload -
Ensure that you have root access and add the following service and timer files to the
/etc/systemd/systemdirectory (set their ownerships to theyugabyteuser and 0644 permissions):yb-master.service[Unit] Description=Yugabyte master service Requires=network-online.target After=network.target network-online.target multi-user.target StartLimitInterval=100 StartLimitBurst=10 [Path] PathExists=/home/yugabyte/master/bin/yb-master PathExists=/home/yugabyte/master/conf/server.conf [Service] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte # Start ExecStart=/home/yugabyte/master/bin/yb-master --flagfile /home/yugabyte/master/conf/server.conf Restart=on-failure RestartSec=5 # Stop -> SIGTERM - 10s - SIGKILL (if not stopped) [matches existing cron behavior] KillMode=process TimeoutStopFailureMode=terminate KillSignal=SIGTERM TimeoutStopSec=10 FinalKillSignal=SIGKILL # Logs StandardOutput=syslog StandardError=syslog # ulimit LimitCORE=infinity LimitNOFILE=1048576 LimitNPROC=12000 [Install] WantedBy=default.targetyb-tserver.service[Unit] Description=Yugabyte tserver service Requires=network-online.target After=network.target network-online.target multi-user.target StartLimitInterval=100 StartLimitBurst=10 [Path] PathExists=/home/yugabyte/tserver/bin/yb-tserver PathExists=/home/yugabyte/tserver/conf/server.conf [Service] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte # Start ExecStart=/home/yugabyte/tserver/bin/yb-tserver --flagfile /home/yugabyte/tserver/conf/server.conf Restart=on-failure RestartSec=5 # Stop -> SIGTERM - 10s - SIGKILL (if not stopped) [matches existing cron behavior] KillMode=process TimeoutStopFailureMode=terminate KillSignal=SIGTERM TimeoutStopSec=10 FinalKillSignal=SIGKILL # Logs StandardOutput=syslog StandardError=syslog # ulimit LimitCORE=infinity LimitNOFILE=1048576 LimitNPROC=12000 [Install] WantedBy=default.targetyb-zip_purge_yb_logs.service[Unit] Description=Yugabyte logs Wants=yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.timer [Service] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte Type=oneshot WorkingDirectory=/home/yugabyte/bin ExecStart=/bin/sh /home/yugabyte/bin/zip_purge_yb_logs.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetyb-zip_purge_yb_logs.timer[Unit] Description=Yugabyte logs Requires=yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.service [Timer] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte Unit=yb-zip_purge_yb_logs.service # Run hourly at minute 0 (beginning) of every hour OnCalendar=00/1:00 [Install] WantedBy=timers.targetyb-clean_cores.service[Unit] Description=Yugabyte clean cores Wants=yb-clean_cores.timer [Service] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte Type=oneshot WorkingDirectory=/home/yugabyte/bin ExecStart=/bin/sh /home/yugabyte/bin/clean_cores.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetyb-controller.service[Unit] Description=Yugabyte Controller Requires=network-online.target After=network.target network-online.target multi-user.target StartLimitInterval=100 StartLimitBurst=10 [Path] PathExists=/home/yugabyte/controller/bin/yb-controller-server PathExists=/home/yugabyte/controller/conf/server.conf [Service] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte # Start ExecStart=/home/yugabyte/controller/bin/yb-controller-server \ --flagfile /home/yugabyte/controller/conf/server.conf Restart=always RestartSec=5 # Stop -> SIGTERM - 10s - SIGKILL (if not stopped) [matches existing cron behavior] KillMode=control-group TimeoutStopFailureMode=terminate KillSignal=SIGTERM TimeoutStopSec=10 FinalKillSignal=SIGKILL # Logs StandardOutput=syslog StandardError=syslog # ulimit LimitCORE=infinity LimitNOFILE=1048576 LimitNPROC=12000 [Install] WantedBy=default.targetyb-clean_cores.timer[Unit] Description=Yugabyte clean cores Requires=yb-clean_cores.service [Timer] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte Unit=yb-clean_cores.service # Run every 10 minutes offset by 5 (5, 15, 25...) OnCalendar=*:0/10:30 [Install] WantedBy=timers.targetyb-collect_metrics.service[Unit] Description=Yugabyte collect metrics Wants=yb-collect_metrics.timer [Service] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte Type=oneshot WorkingDirectory=/home/yugabyte/bin ExecStart=/bin/bash /home/yugabyte/bin/collect_metrics_wrapper.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetyb-collect_metrics.timer[Unit] Description=Yugabyte collect metrics Requires=yb-collect_metrics.service [Timer] User=yugabyte Group=yugabyte Unit=yb-collect_metrics.service # Run every 1 minute OnCalendar=*:0/1:0 [Install] WantedBy=timers.targetyb-bind_check.service[Unit] Description=Yugabyte IP bind check Requires=network-online.target After=network.target network-online.target multi-user.target Before=yb-controller.service yb-tserver.service yb-master.service yb-collect_metrics.timer StartLimitInterval=100 StartLimitBurst=10 [Path] PathExists=/home/yugabyte/controller/bin/yb-controller-server PathExists=/home/yugabyte/controller/conf/server.conf [Service] # Start ExecStart=/home/yugabyte/controller/bin/yb-controller-server \ --flagfile /home/yugabyte/controller/conf/server.conf \ --only_bind --logtostderr Type=oneshot KillMode=control-group KillSignal=SIGTERM TimeoutStopSec=10 # Logs StandardOutput=syslog StandardError=syslog [Install] WantedBy=default.target
Use node agents
To automate some of the steps outlined in Provision nodes manually, YugabyteDB Anywhere provides a node agent that you can run on each node meeting the following requirements:
- The node has already been set up with the
yugabyteuser group and home. - The bi-directional communication between the node and YugabyteDB Anywhere has been established (that is, the IP address can reach the host and vice versa).
Installation
You can install a node agent as follows:
-
Download the installer from YugabyteDB Anywhere using the API token of the Super Admin, as follows:
curl https://<yugabytedb_anywhere_address>/api/v1/node_agents/download --fail --header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: <api_token>' > installer.sh && chmod +x installer.sh -
Verify that the installer file contains the script.
-
Run the following command to download the node agent's
.tgzfile which installs and starts the interactive configuration:./installer.sh -c install -u https://<yugabytedb_anywhere_address> -t <api_token>For example, if you execute
./installer.sh -c install -u http://100.98.0.42:9000 -t 301fc382-cf06-4a1b-b5ef-0c8c45273aef, expect the following output:* Starting YB Node Agent install * Creating Node Agent Directory * Changing directory to node agent * Creating Sub Directories * Downloading YB Node Agent build package * Getting Linux/amd64 package * Downloaded Version - 2.17.1.0-PRE_RELEASE * Extracting the build package * The current value of Node IP is not set; Enter new value or enter to skip: 10.9.198.2 * The current value of Node Name is not set; Enter new value or enter to skip: Test * Select your Onprem Provider 1. Provider ID: 41ac964d-1db2-413e-a517-2a8d840ff5cd, Provider Name: onprem Enter the option number: 1 * Select your Instance Type 1. Instance Code: c5.large Enter the option number: 1 * Select your Region 1. Region ID: dc0298f6-21bf-4f90-b061-9c81ed30f79f, Region Code: us-west-2 Enter the option number: 1 * Select your Zone 1. Zone ID: 99c66b32-deb4-49be-85f9-c3ef3a6e04bc, Zone Name: us-west-2c Enter the option number: 1 • Completed Node Agent Configuration • Node Agent Registration Successful You can install a systemd service on linux machines by running sudo node-agent-installer.sh -c install-service --user yugabyte (Requires sudo access). -
Run the following command to enable the node agent as a systemd service, which is required for self-upgrade and other functions:
sudo node-agent-installer.sh -c install-service --user yugabyte
When the installation has been completed, the configurations are saved in the config.yml file located in the node-agent/config/ directory. You should refrain from manually changing values in this file.
Registration
To enable secured communication, the node agent is automatically registered during its installation so the YugabyteDB Anywhere is aware of its existence. You can also register and unregister the node agent manually during configuration.
The following is the node agent registration command:
node-agent node register --api-token <api_token>
If you need to overwrite any previously configured values, you can use the following parameters in the registration command:
--node_iprepresents the node IP address.--urlrepresents the YugabyteDB Anywhere address.
For secured communication, YugabyteDB Anywhere generates a key pair (private, public, and server certificate) that is sent to the node agent as part of its registration process.
To unregister a node agent, use the following command:
node-agent node unregister
Operations
Even though the node agent installation, configuration, and registration are sufficient, the following supplementary commands are also supported:
node-agent node unregisteris used for un-registering the node and node agent from YugabyteDB Anywhere. This can be done to restart the registration process.node-agent node registeris used for registering a node and node agent to YugabyteDB Anywhere if they were unregistered manually. Registering an already registered node agent fails as YugabyteDB Anywhere keeps a record of the node agent with this IP.node-agent service startandnode-agent service stopare used for starting or stopping the node agent as a gRPC server.node-agent node preflight-checkis used for checking if a node is configured as a YugabyteDB Anywhere node. After the node agent and the node have been registered with YugabyteDB Anywhere, this command can be run on its own, if the result needs to be published to YugabyteDB Anywhere. For more information, see Preflight check.
Preflight check
After the node agent is installed, configured, and connected to YugabyteDB Anywhere, you can perform a series of preflight checks without sudo privileges by using the following command:
node-agent node preflight-check
The result of the check is forwarded to YugabyteDB Anywhere for validation. The validated information is posted in a tabular form on the terminal. If there is a failure against a required check, you can apply a fix and then rerun the preflight check.
Expect an output similar to the following:
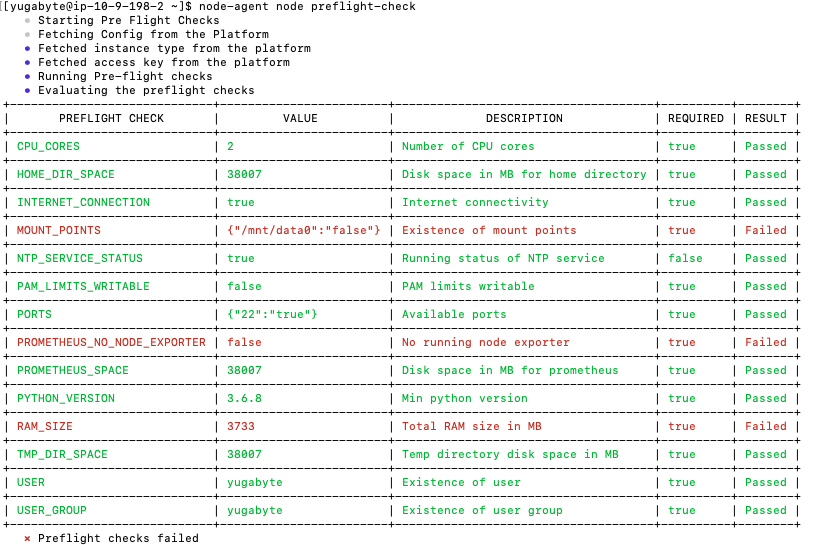
If the preflight check is successful, you would be able to add the node to the provider (if required) by executing the following:
node-agent node preflight-check --add_node
Remove YugabyteDB components from the server
As described in Eliminate an unresponsive node, when a node enters an undesirable state, you can delete such node, with YugabyteDB Anywhere clearing up all the remaining artifacts except the prometheus and yugabyte user.
You can manually remove Yugabyte components from existing server images. Before attempting this, you have to determine whether or not YugabyteDB Anywhere is operational. If it is, you either need to delete the universe or delete the nodes from the universe.
To completely eliminate all traces of YugabyteDB Anywhere and configuration, you should consider reinstalling the operating system image (or rolling back to a previous image, if available).
Delete database server nodes
You can remove YugabyteDB components and configuration from the database server nodes as follows:
-
Login to the server node as the
yugabyteuser. -
Navigate to the
/home/yugabyte/bindirectory that contains a number of scripts includingyb-server-ctl.sh. The arguments set in this script allow you to perform various functions on the YugabyteDB processes running on the node. -
Execute the following command:
./bin/yb-server-ctl.sh clean-instanceThis removes all YugabyteDB code and settings from the node, removing it from the Universe.
If you cannot find the
bindirectory, it means YugabyteDB Anywhere already cleared it during a successful deletion of the universe.
You should also erase the data from the volume mounted under the /data subdirectory, unless this volume is to be permanently erased by the underlying storage subsystem when the volume is deleted.
To erase this data, execute the following commands from the centos user on the node (or any user with access to sudo):
sudo umount /data
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdb bs=1M
The preceding commands assume the data volume is attached to the server as /dev/sdb.
If there is a requirement to remove the yugabyte user, execute the following command:
sudo userdel -r yugabyte
If there is a requirement to remove the prometheus user, execute the following command:
sudo rm -rf /opt/prometheus
You may now choose to reverse the system settings that you configured in Provision nodes manually.
Delete YugabyteDB Anywhere from the server
To remove YugabyteDB Anywhere and Replicated components from the host server, execute the following commands as the root user (or prepend sudo to each command) :
systemctl stop replicated replicated-ui replicated-operator
service replicated stop
service replicated-ui stop
service replicated-operator stop
docker stop replicated-premkit
docker stop replicated-statsd
docker rm -f replicated replicated-ui replicated-operator replicated-premkit replicated-statsd retraced-api retraced-processor retraced-cron retraced-nsqd retraced-postgres
docker images | grep "quay.io/replicated" | awk '{print $3}' | xargs sudo docker rmi -f
docker images | grep "registry.replicated.com/library/retraced" | awk '{print $3}' | xargs sudo docker rmi -f
yum remove -y replicated replicated-ui replicated-operator
rm -rf /var/lib/replicated* /etc/replicated* /etc/init/replicated* /etc/default/replicated* /etc/systemd/system/replicated* /etc/sysconfig/replicated* /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/replicated* /run/replicated*
rpm -qa | grep -i docker
yum remove docker-ce
rpm -qa | grep -i docker
yum remove docker-ce-cli
Finally, execute the following commands to delete the /opt/yugabyte directory on the node to prevent failure if later you decide to install YugabyteDB Anywhere on a node that was previously removed using the preceding instructions:
rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
rm -rf /home/replicated
rm -rf /opt/containerd
rm -rf /opt/yugabyte