Install YugabyteDB Anywhere
Use the following instructions to install YugabyteDB Anywhere software. For guidance on which method to choose, see YBA Prerequisites.
Note: For higher availability, one or more additional YugabyteDB Anywhere instances can be separately installed, and then configured later to serve as passive warm standby servers. See Enable High Availability for more information.
To install YugabyteDB Anywhere on an OpenShift cluster, you can use YugabyteDB Anywhere Operator or the Helm tool.
Note
As YugabyteDB Anywhere was formerly called Yugabyte Platform, you might see the latter still used in the OpenShift environment.Prerequisites
Before you install YugabyteDB Anywhere on an OpenShift cluster, you need to prepare the environment, as described in Prepare the OpenShift environment.
Unless otherwise specified, you can use a user account for executing the steps described in this document. Using admin account for all the steps should work as well.
Operator-based installation
Installing YugabyteDB Anywhere on an OpenShift cluster using the YugabyteDB Anywhere Operator involves the following:
- Installing the Operator itself
- Creating an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere
- Finding the availability zone labels
- Configuring the CLI with the OCP cluster
- Accessing and configuring YugabyteDB Anywhere
- Optionally, upgrading the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance
Install the Operator
You can install the YugabyteDB Anywhere Operator via the OpenShift web console or command line.
Use the OpenShift web console
You can install the YugabyteDB Anywhere Operator as follows:
-
Login to the OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) cluster's web console using admin credentials (for example, kube:admin).
-
Navigate to the Operators > OperatorHub, search for YugabyteDB Anywhere Operator, and then open it to display details about the operator, as shown in the following illustration:
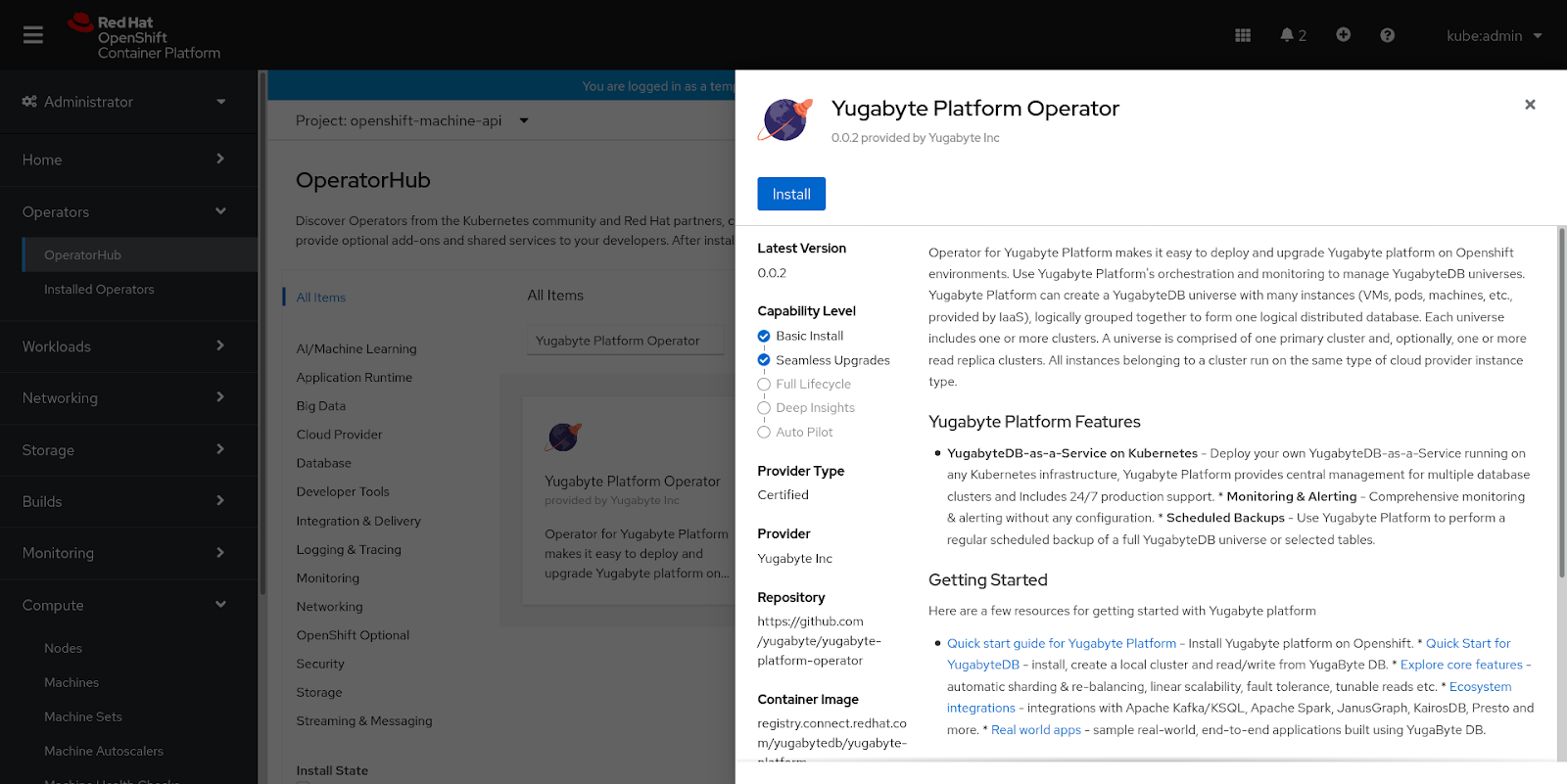
-
Click Install.
-
Accept default settings on the Install Operator page, as shown in the following illustration, and then click Install.
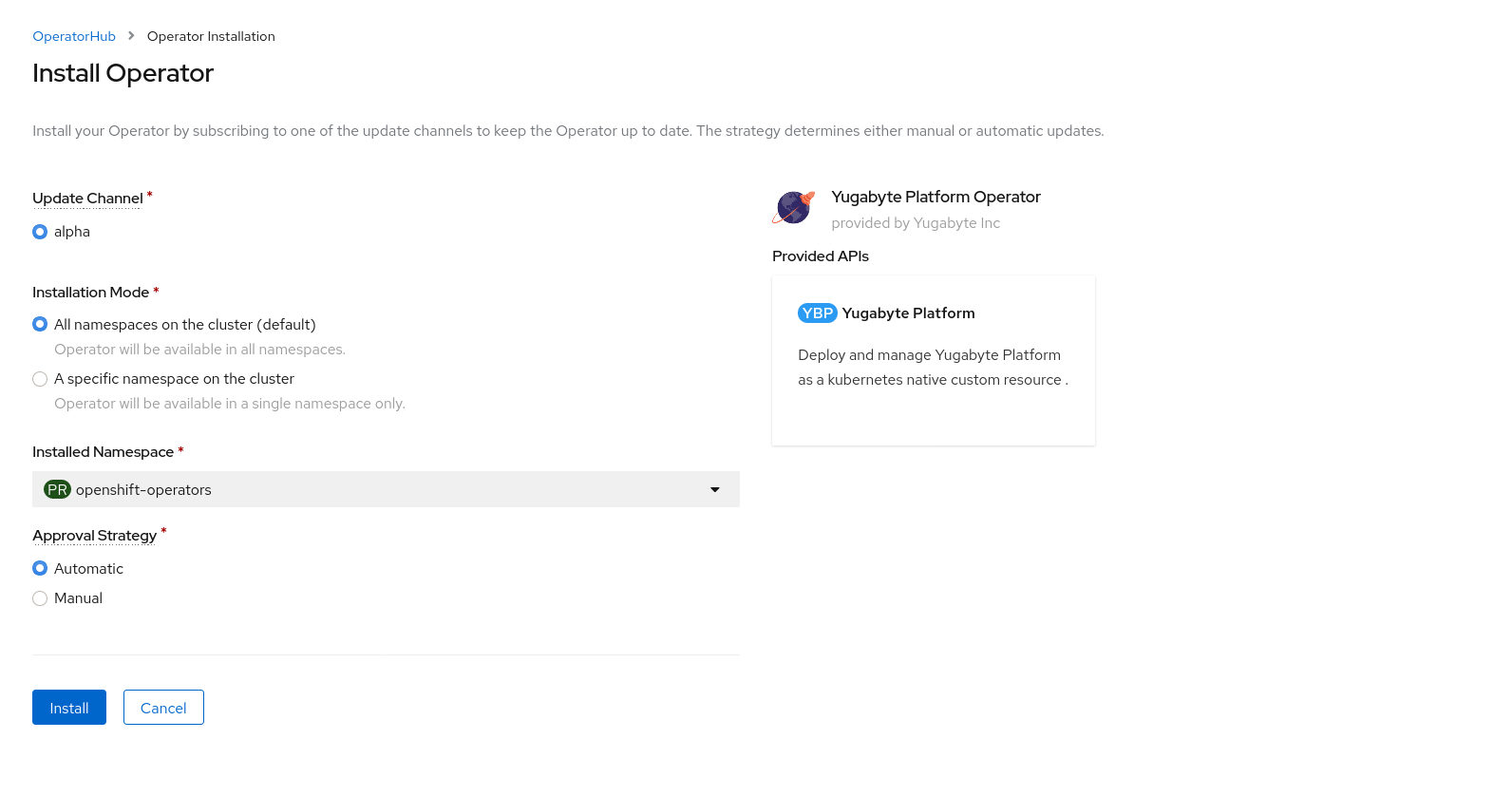
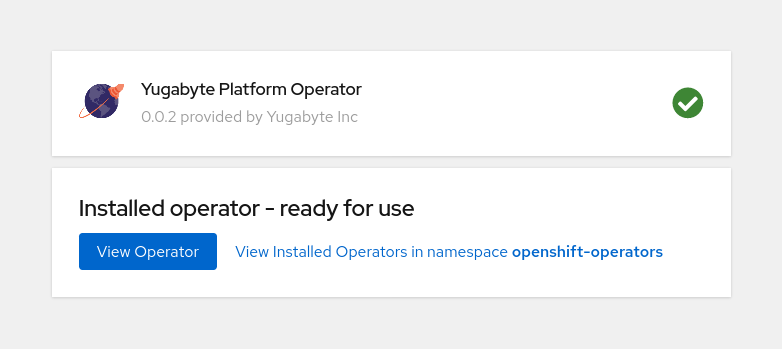
After the installation is complete, the message shown in the following illustration is displayed:
Use the command line
Alternatively, you can install the operator via the command line. You start by configuring oc with an admin account (kube:admin) and following the procedure described in Configure oc with the OCP Cluster.
To install the YugabyteDB Anywhere Operator, execute the following command:
oc apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: yugabyte-platform-operator-bundle
namespace: openshift-operators
spec:
channel: alpha
name: yugabyte-platform-operator-bundle
source: certified-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
EOF
This creates a Subscription object and installs the operator in the cluster, as demonstrated by the following output:
subscription.operators.coreos.com/yugabyte-platform-operator-bundle created
To verify that the operator pods are in Running state, execute the following command:
oc get pods -n openshift-operators | grep -E '^NAME|yugabyte-platform'
Expect the following output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
yugabyte-platform-operator-controller-manager-7485db7486-6nzxr 2/2 Running 0 5m38s
For additional information, see Adding operators to a cluster.
Create an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere via Operator
You start by creating an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere in a new project (namespace) called yb-platform. To do this, you can use the OpenShift web console or command line.
Use the OpenShift web console
You can create an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere via the OpenShift web console as follows:
-
Open the OCP web console and navigate to Home > Projects > Create Project.
-
Enter the name yb-platform and click Create.
-
Navigate to Operators > Installed Operators and select YugabyteDB Anywhere Operator, as shown in the following illustration:
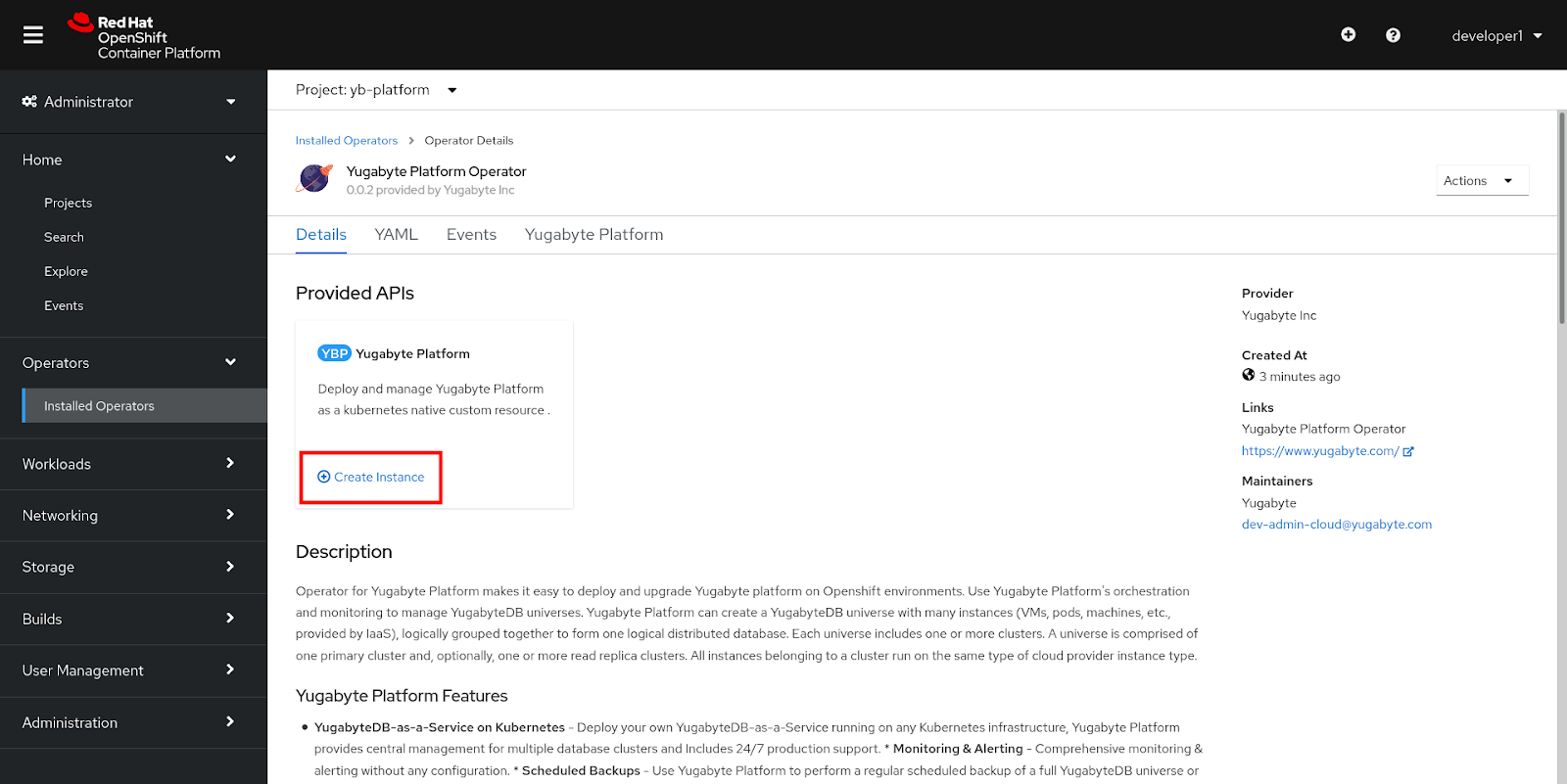
-
Click Create Instance to open the Create YBPlatform page.
-
Ensure that the yb-platform project is selected and review the default settings.
-
Accept the default settings without modifying them, unless your cluster has a StorageClass other than standard, in which case open YAML View and change the value of
spec.yugaware.storageClassto the correct StorageClass name.You can find the StorageClass by navigating to Storage > Storage Classes on the OpenShift Web Console as admin user.
-
Click Create.
Shortly, you should expect the Status column in the YugabyteDB Anywhere tab to display Deployed, as shown in the following illustration:
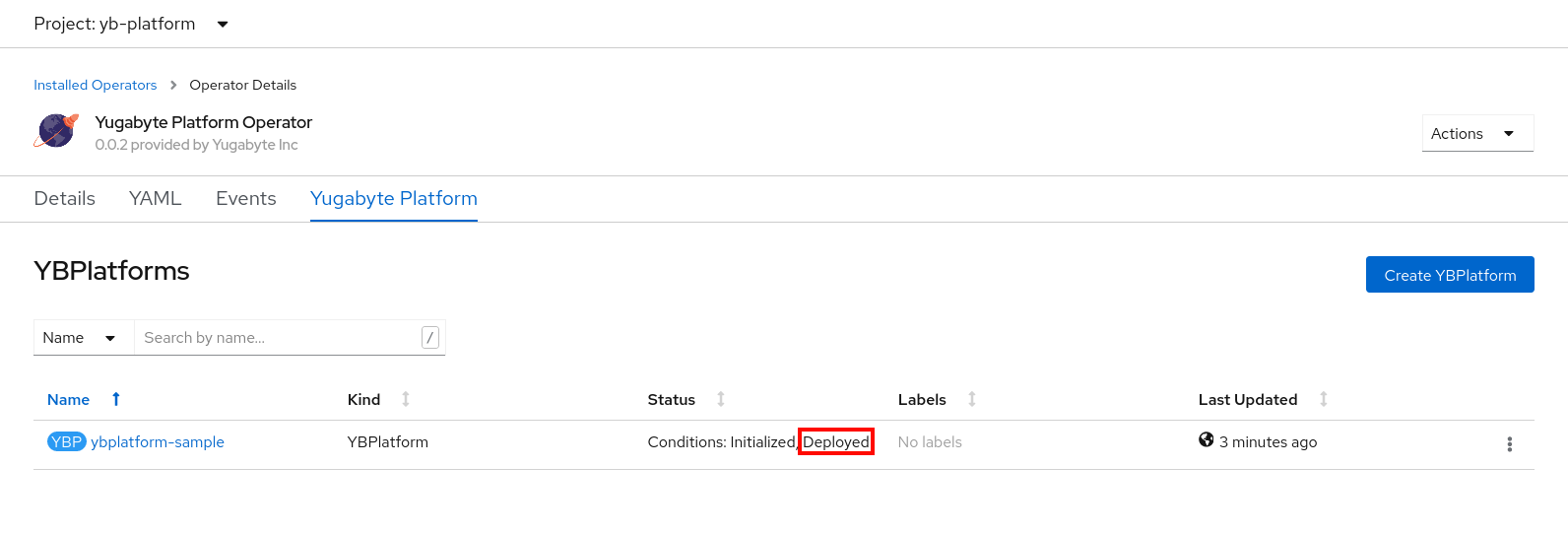
Use the command line
Alternatively, you can create an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere via the command line, as follows:
-
To create a new project, execute the following command:
oc new-project yb-platformExpect the following output:
Now using project "yb-platform" on server "web-console-address" -
Verify the StorageClass setting for your cluster by executing the following command as admin user:
oc get storageClassIf your cluster's StorageClass is not
standard, change the value ofspec.yugaware.storageClassto the correct StorageClass name when you create an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere. -
To create an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere in the yb-platform project, execute the following command:
oc apply \ -n yb-platform \ -f - <<EOF apiVersion: yugabyte.com/v1alpha1 kind: YBPlatform metadata: name: ybplatform-sample spec: image: repository: registry.connect.redhat.com/yugabytedb/yugabyte-platform tag: latest ocpCompatibility: enabled: true rbac: create: false EOFExpect the following output:
ybplatform.yugabyte.com/ybplatform-sample created -
To verify that the pods of the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance are in Running state, execute the following:
oc get pods -n yb-platform -l app=ybplatform-sample-yugawareExpect the following output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE Ybplatform-sample-yugaware-0 5/5 Running 0 22s
Upgrade the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance
You may choose to upgrade the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance installed using the Operator to a new tag that you receive from Yugabyte. In the current release, you can do this by using the command line.
The following example shows the command you would execute to update the container image tag to 2.5.2.0-b89:
oc patch \
ybplatform ybplatform-sample \
-p '{"spec":{"image":{"tag":"2.5.2.0-b89"}}}' --type merge \
-n yb-platform
Expect the following output:
ybplatform.yugabyte.com/ybplatform-sample patched
To verify that the pods are being updated, execute the following command:
oc get pods -n yb-platform -l app=ybplatform-sample-yugaware -w
Expect the following output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ybplatform-sample-yugaware-0 5/5 Running 0 18m
ybplatform-sample-yugaware-0 0/5 Terminating 0 19m
ybplatform-sample-yugaware-0 0/5 Pending 0 0s
ybplatform-sample-yugaware-0 0/5 ContainerCreating 0 35s
ybplatform-sample-yugaware-0 5/5 Running 0 93s
Helm-based installation
In addition to meeting the requirements described in Prepare the OpenShift Environment, you need to perform the following steps before attempting to install YugabyteDB Anywhere using Helm:
-
Verify that the OpenShift cluster is configured with Helm 3.4 or later by executing the following command:
helm versionThe output should be similar to the following:
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.2.1", GitCommit:"fe51cd1e31e6a202cba7dead9552a6d418ded79a", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.13.10" -
Ensure that an OpenShift secret license file has been obtained from Yugabyte Support.
Installing YugabyteDB Anywhere on an OpenShift cluster using Helm involves the following:
- Creating an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere
- Finding the availability zone labels
- Configuring the CLI with the OCP cluster
- Accessing and configuring YugabyteDB Anywhere
Create an instance of YugabyteDB Anywhere via Helm
To create a YugabyteDB Anywhere instance, perform the following:
-
Create a new project (namespace) called yb-platform by executing the following command:
oc new-project yb-platformExpect the following output:
Now using project "yb-platform" on server "web-console-address" -
Apply the YugabyteDB Anywhere secret that you obtained from Yugabyte Support by executing the following command:
oc create -f yugabyte-k8s-secret.yml -n yb-platformExpect the following output:
secret/yugabyte-k8s-pull-secret created -
Execute the following command to add the YugabyteDB charts repository:
helm repo add yugabytedb https://charts.yugabyte.comExpect the following output:
"yugabytedb" has been added to your repositoriesTo search for the available chart version, execute the following command:
helm search repo yugabytedb/yugaware --version 2.17.3Expect the following output:
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION yugabytedb/yugaware 2.17.3 2.17.3.0-b152 YugaWare is YugaByte Database's Orchestration a... -
Verify the StorageClass setting for your cluster by executing the following command as admin user:
oc get storageClassIf your cluster's StorageClass is not
standard, add--set yugaware.storageClass=<storage-class-name>when installing the YugabyteDB Anywhere Helm chart in the next step. -
Execute the following command to install the YugabyteDB Anywhere Helm chart:
helm install yw-test yugabytedb/yugaware -n yb-platform \ --version 2.17.3 \ --set image.repository=quay.io/yugabyte/yugaware-ubi \ --set ocpCompatibility.enabled=true --set rbac.create=false \ --set securityContext.enabled=false --waitExpect to see a message notifying you whether or not the deployment is successful.
Note that if you are executing the preceding command as an admin user, then you can set
rbac.create=true. Alternatively, you can ask the cluster administrator to perform the next step. -
Optionally, execute the following command as an admin user to create ClusterRoleBinding:
oc apply -f - <<EOF kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: yw-test-cluster-monitoring-view labels: app: yugaware subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: yw-test namespace: yb-platform roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-monitoring-view apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io EOF- ClusterRole or ClusterRoleBinding with the cluster-admin role are recommended if your intention is to create clusters across multiple namespaces.
- Certain container-level metrics like CPU, memory will be unavailable without the above
ClusterRoleBinding.
Delete the Helm installation of YugabyteDB Anywhere
You can delete the Helm installation by executing the following command:
helm delete yw-test -n yb-platform
Find the availability zone labels
You need to find the region name and availability zone codes where the cluster is running. This information is required by YugabyteDB Anywhere (see Create a Provider in YugabyteDB Anywhere). For example, if your OCP cluster is in the US East, then the cloud provider's zone labels can be us-east4-a, us-east4-b, and so on.
You can use the OpenShift web console or the command line to search for the availability zone codes.
Use the OpenShift web console
You start by logging in the OCP's web console as admin user, and then performing the following:
-
Navigate to Compute > Machine Sets and open each Machine Set.
-
On the Machine Set Details page, open the Machines tab to access the region and availability zone label, as shown in the following illustration where the region is US East and the availability zone label is us-east4-a:
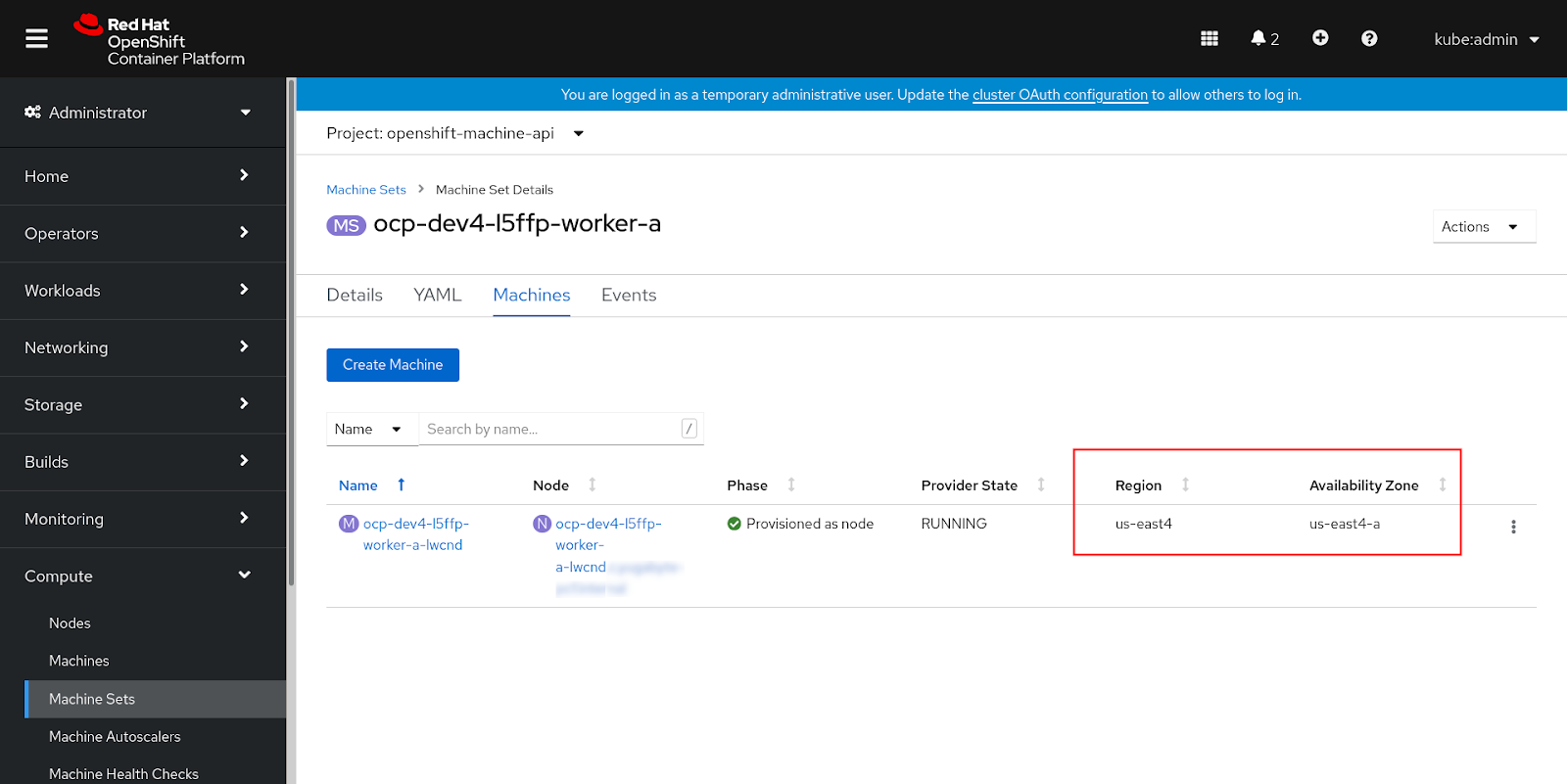
Use the command line
Alternatively, you can find the availability zone codes via the command line.
You start by configuring oc with an admin account (kube:admin) and following the procedure described in Configure oc with the OCP Cluster.
To find the region and zone labels, execute the following command:
oc get machinesets \
-n openshift-machine-api \
-ojsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{", region: "}{.spec.template.spec.providerSpec.value.region}{", zone: "}{.spec.template.spec.providerSpec.value.zone}{"\n"}{end}'
Expect the following output:
ocp-dev4-l5ffp-worker-a, region: us-east4, zone: us-east4-a
ocp-dev4-l5ffp-worker-b, region: us-east4, zone: us-east4-b
ocp-dev4-l5ffp-worker-c, region: us-east4, zone: us-east4-c
After the execution, the region is displayed as US East and the zones as us-east4-a, us-east4-b, and so on.
Configure the CLI with the OCP cluster
To configure the OpenShift command-line interface (CLI) tool oc, you start by logging in to the OCP web console with your user account. For more information and specific instructions, see Getting Started with the CLI.
Access and configure YugabyteDB Anywhere
After you have created and deployed YugabyteDB Anywhere, you can access its web UI and create an account.
Find the location to access the web UI
To find the location (IP address or hostname), you can use the OpenShift web console or the command line.
Use the OpenShift web console
You can obtain the location using the OpenShift web console as follows:
-
Use the OCP web console to navigate to Networking > Services and select ybplatform-sample-yugaware-ui from the list. Ensure that the yb-platform project is selected.
-
In the Service Routing section of the Details tab, locate External Load Balancer and copy the value, as shown in the following illustration:
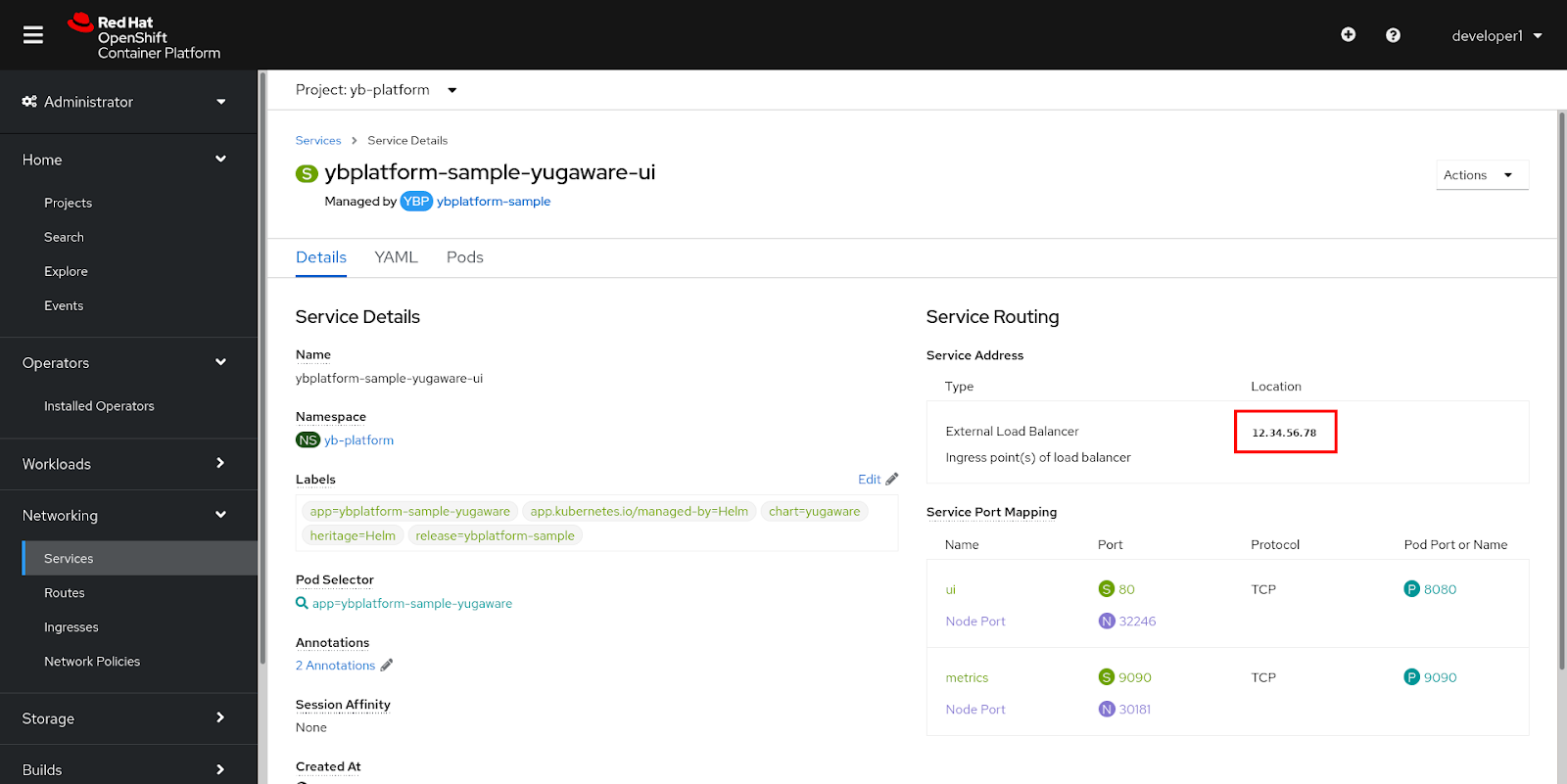
-
Open the copied location in a new instance of your web browser.
Use the command line
Alternatively, you can obtain the information about the location via the command line.
In case of the Operator-based installation of YugabyteDB Anywhere, execute the following command:
oc get services \
ybplatform-sample-yugaware-ui \
-ojsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}{"\n"}
{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}{"\n"}'
Expect the following output:
12.34.56.78
In case of the Helm-based installation, execute the following command:
oc get services \
yw-test-yugaware-ui \
-ojsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}{"\n"}
{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}{"\n"}'
Expect the following output:
12.34.56.78