Overview
Before you get started, decide whether you are deploying on Public cloud, On-premises, or Kubernetes. In public cloud, YugabyteDB Anywhere (YBA) creates and launches virtual machine (VM) instances on the cloud to become nodes in a YugabyteDB universe, and YBA needs permissions to create VMs. In On-premises, you manually create VMs, and then provide the hostnames of these VMs to YBA, where they become "free nodes" to be used in creating universes.
All of these process flows follow the same general steps:
- Install and configure YugabyteDB Anywhere.
- Create a Provider Configuration (choose among AWS, GCP, Azure, on-prem, or various Kubernetes options).
- Create a Universe using the configuration.
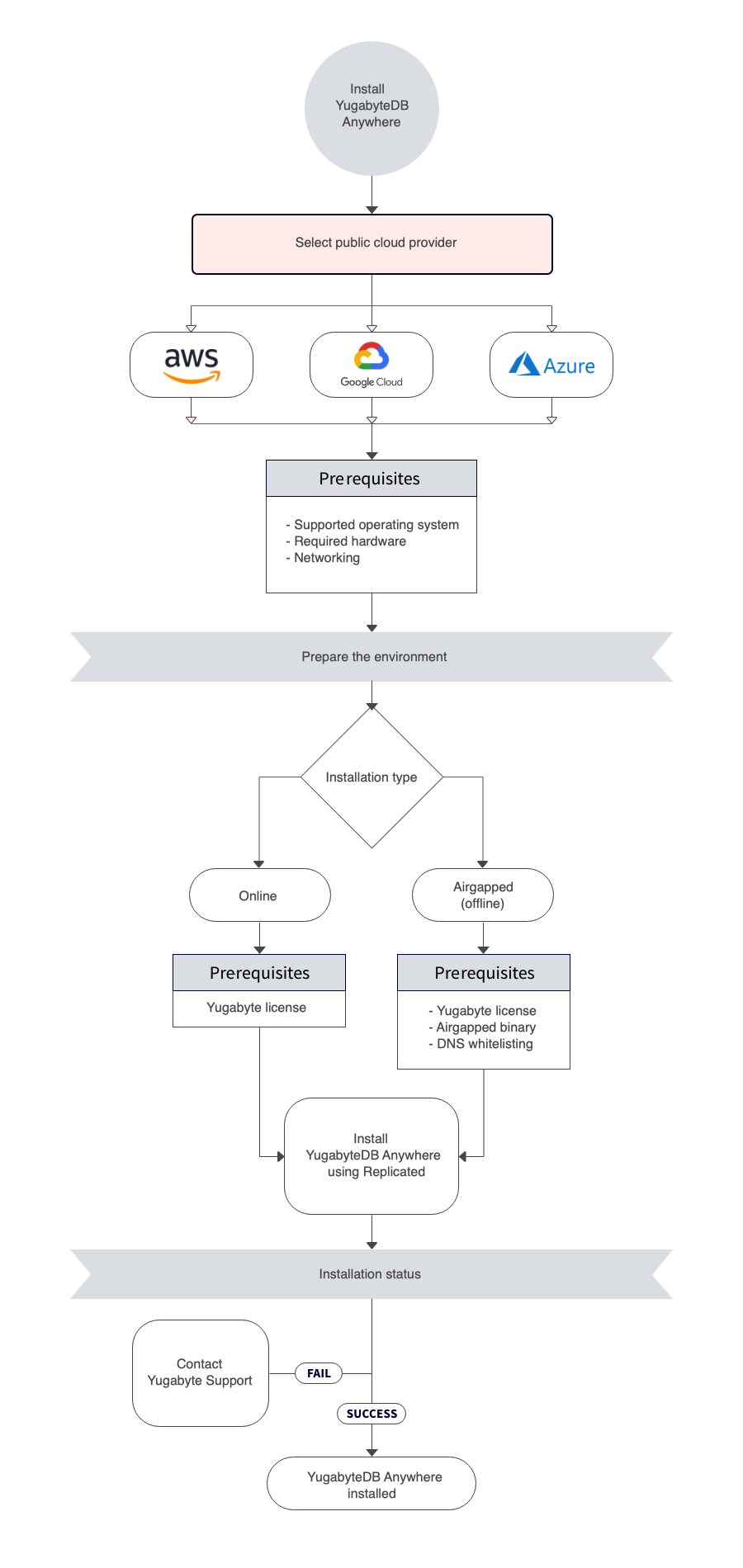
The following diagram shows the YugabyteDB Anywhere installation process in a public cloud. Click elements of the chart to access detailed steps.
Note: If you are using a public cloud such as AWS, GCP, or Azure, but you cannot grant YBA permissions (or a service account) to create VMs on your public cloud, use the On-premises workflow instead. In this case you would manually create VMs on your public cloud, and then provide the hostnames of these VMs to YBA.